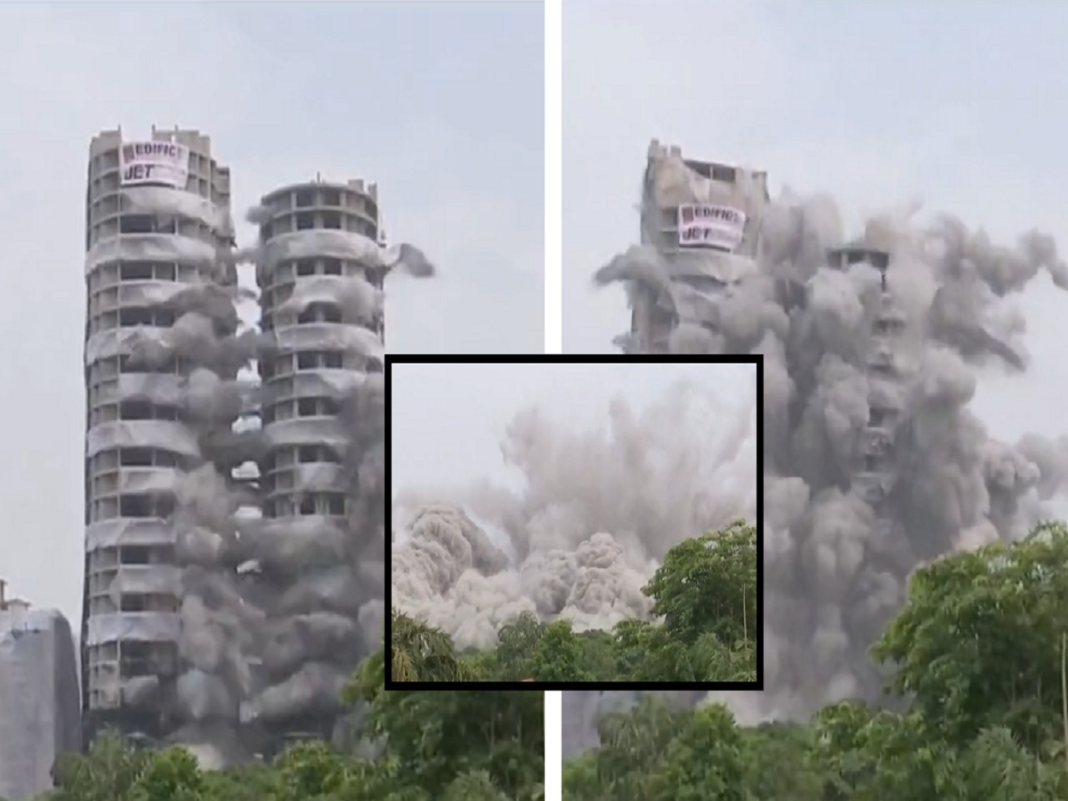
After a nine-year-long legal battle, the Supertech twin towers of Noida were reduced to rubble on Sunday (August 28). The towers, Ceyane (29 floors) and Apex (32 floors), that are part of the Emerald Court project of Supertech Ltd, were found to be in violation of multiple regulations regarding construction, and were therefore demolished.The demolition was ordered by the Supreme Court after the court found their construction on the Emerald Court society premises in violation of norms. The buildings will be demolished by the company at its own expense under the guidance of the Noida Authority. Mumbai-based Edifice Engineering was in charge of the demolition work.
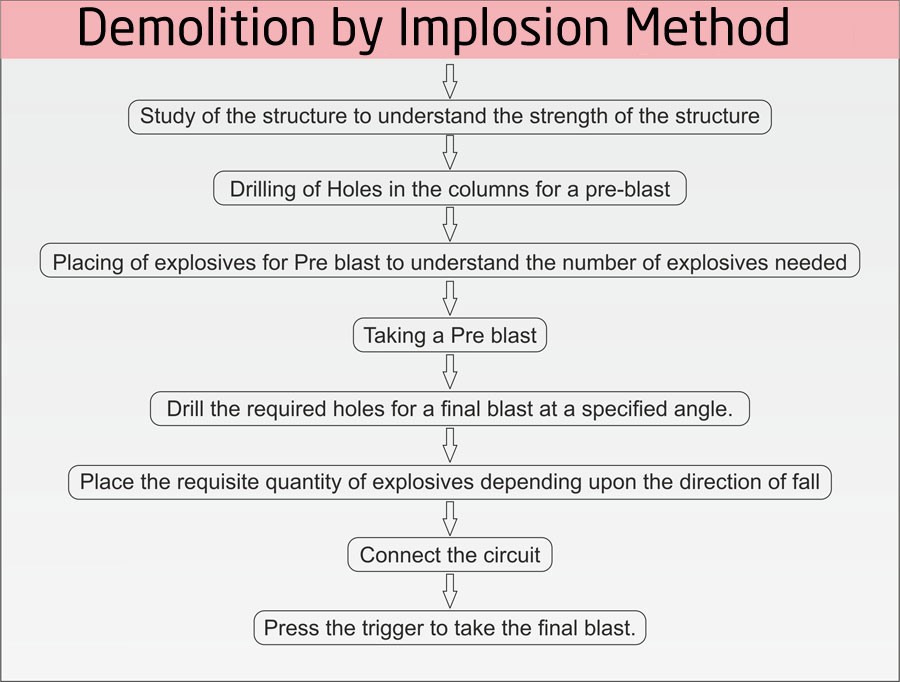
The technique used; Implosion Demolition
The Supertech towers were demolished via a ‘controlled implosion’. Implosion is the strategic placing of explosive material and timing of its detonation so that a structure collapses on itself in a matter of seconds, minimizing the physical damage to its immediate surroundings.
The process behind the implosion included the gradual weakening of critical supports of the building, i.e., removing the structures that will help resist the gravitational force. This will be achieved by numerous explosives placed within the structure.
How Implosion Demolition is executed?
Before the execution of demolition work, the careful study of site condition, the type of structure, structural member, implosion range, rural or urban area and frequency is important. All implosions will need some sort of pressure from the outside pushing in to cause the object to collapse. So in short, implosions are caused by having greater pressure on the outside of an object than on the inside. The technique is discussed below.
- The first step is to examine architectural blueprints of the building, if they can be located, to determine how the building is put together. Next, the blaster crew tours the building (several times), jotting down notes about the support structure on each floor. Once they have gathered all the raw data they need, the blasters hammer out a plan of attack.
- Numerous small explosives, strategically placed within the structure, are used to catalyze the collapse. Nitroglycerin, dynamite, or other explosives are used to shatter reinforced concrete supports. Linear shaped charges are used to sever steel supports.
- These explosives are progressively detonated on support throughout the structure. Then, explosives on the lower floors initiate the controlled collapse.
- Demolition blasters load explosives on several different levels of the building so that the building structure falls down on itself at multiple points.
- When everything is planned and executed correctly, the total damage of the explosives and falling building material is sufficient to collapse the structure entirely, so cleanup crews are left with only a pile of rubble.
- Blasters approach each project a little differently, but the basic idea is to think of the building as a collection of separate towers. The blasters set the explosives so that each “tower” falls toward the center of the building, in roughly the same way that they would set the explosives to topple a single structure to the side.
- When the explosives are detonated in the right order, the toppling towers crash against each other, and all of the rubble collects at the center of the building. Another option is to detonate the columns at the center of the building before the other columns so that the building’s sides fall inward
Stages of the demolition of the Supertech twin tower
- The pre-analysis- Factoring in the design of the buildings, its compressive strength, placement analysis of columns and beams, construction material being and the distance of nearby buildings
- Removing the concrete- narrowing down the structure to columns and beams and removing extra concrete
- Creating cushion- Impact cushions were created in the basement using the debris generated
- Drilling- 9622 holes were drilled in shear walls for explosives. The diameter of each hole was 35mm
- Covering- Shear walls and floors were wrapped with 225 tonnes of iron mesh and geotextile cloth
- Placing of explosives- explosives were placed in shear with charging process and placed in sequence as brought in instalments
- Final demolition; detonators were connected to the charges and button was pressed at 2.30 pm

Detailed analysis of Supertech twin tower;
The tower had 11 primary blast floors – where all columns on the floor will have explosives fixed and blasted — and seven secondary floors – where 40 percent of the columns will be blasted.
- Cayenne and Apex came down simultaneously as charges were triggered in cascade, bottom to the top
- Floors collapsed in series
- Primary blast floors-Charges were placed in all columns
- Secondary blast floors- Charges were placed in 40 percent of the columns
- 9,400 holes were drilled in the columns and shears of the skeletal structures of the twin towers to bring it crashing down
- About 225 tonnes of wired mesh made of galvanised iron and geo-textile in 110-km length used
- Trenches of 4m were dug at the perimeter to prevent any damage to the nearby building through the shock wave of the explosion.
- Containers were placed between the twin towers and the nearby buildings for extra safety
- Installation of nets, cloth and perimeter curtains used to provide three layers of safety from the dust and debris to the nearby building
What’s next?
Edifice Engineering now has two key tasks ahead: disposing of 80,000 tonnes of debris, and analysing data from accelerometers, black boxes and other scales placed around the demolition site.
Post-demolition 35,000 cubic metres of rubble is expected to be left, a Noida Authority official said. “Of this, 6,000 to 7,000 cubic metres would gather in the basement of twin towers,
The plan for debris management was yet to be finalised as the regional pollution control board was examining the proposal sent by Edifice Engineering. The plan is expected to be finalised in a day or two.
Supertech is paying around Rs 4.5-5.5 crore for the demolition and the rest of the amount, Rs 14.5-15.5 crore is expected to be made by selling off the debris.
If you want to know the reason behind demolition and the technique being used for the demolition, you get all the details at –https://constrofacilitator.com/india-is-set-to-witness-the-biggest-demolition-of-building/





