A building automation system (BAS) is a centralized system that uses technology and software to monitor, control, and optimize various building functions, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning, lighting, security, and other systems. BAS allows for the integration and coordination of these systems, making buildings more energy-efficient, comfortable, and secure. It typically uses sensors, actuators, and a central control unit to automate and manage the building’s operations, providing better control and visibility over different aspects of the building’s performance.
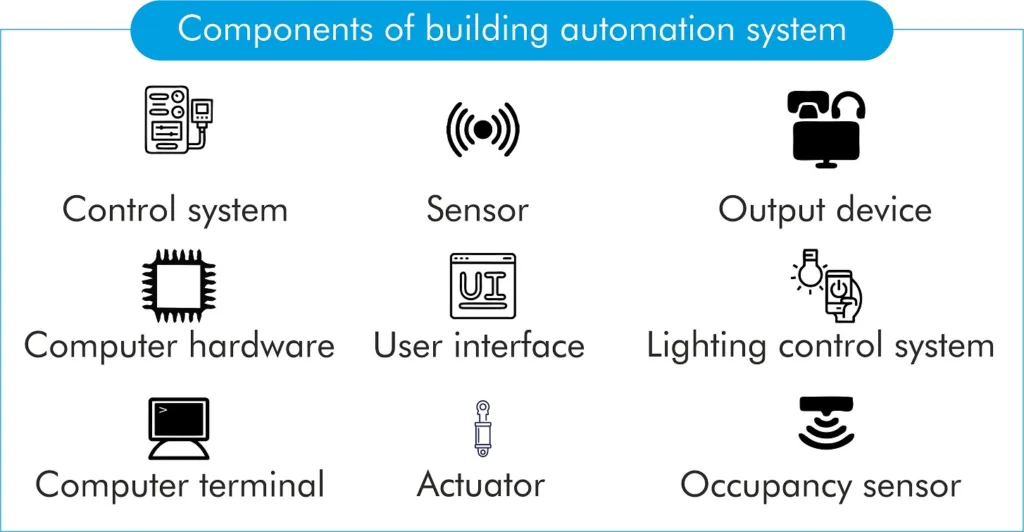
Components of building automation system
The key components of a building automation system (BAS) include:
- Sensors: BAS relies on various sensors to gather data about the building’s environment, such as temperature, humidity, occupancy, light levels, CO2 levels, and more. These sensors provide real-time information to the central control system.
- Actuators: Actuators are devices that respond to commands from the central control system and perform physical actions, such as adjusting thermostats, opening/closing valves, turning on/off lights, or controlling motorized shades.
- Central Control Unit: The central control unit is the brain of the BAS. It processes data from sensors, interprets it, and makes decisions based on predefined algorithms and user settings. The control unit sends commands to actuators to regulate building systems accordingly.
- User Interface: A user interface allows building managers or operators to interact with the BAS. This interface can be a computer software application, a web-based portal, or even a mobile app, providing real-time monitoring and control of building systems.
- HVAC System: The BAS integrates with the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system to optimize temperature and airflow control based on occupancy and environmental conditions, ensuring comfort while reducing energy consumption.
- Lighting Control System: BAS manages lighting levels by controlling the intensity and timing of lights based on occupancy, daylight availability, or user preferences, promoting energy efficiency.
- Energy Management System: This component tracks and analyzes energy consumption patterns, helping building owners identify opportunities to reduce energy usage and improve efficiency.
- Security and Access Control: BAS can integrate with security systems, including access control, surveillance cameras, and intrusion alarms, to ensure building safety and control access to sensitive areas.
- Fire Safety Systems: The BAS can monitor and control fire detection and suppression systems, providing a rapid response to potential emergencies.
- Communication Protocols: Various communication protocols, such as BACnet, Modbus, LonWorks, and others, enable seamless data exchange between different components of the BAS, facilitating interoperability.
- Building Performance Analytics: BAS can include analytics tools to analyze data collected from sensors, identifying patterns, anomalies, and potential optimizations to enhance building performance.
These key components work together to create an interconnected and intelligent building automation system that optimizes building operations, enhances occupant comfort, reduces energy consumption, and improves overall building efficiency and sustainability.
Advantages of building automation system
Building Automation Systems (BAS) offer several advantages for both building owners and occupants:
- Energy Efficiency: BAS optimizes the operation of building systems, such as heating, cooling, and lighting, based on real-time data and occupancy patterns. This results in reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills.
- Cost Savings: By improving energy efficiency and streamlining operations, BAS leads to significant cost savings on energy and maintenance expenses over time.
- Enhanced Comfort: Precise control over HVAC systems and lighting allows for a more comfortable and consistent indoor environment, meeting the preferences of occupants.
- Increased Productivity: A comfortable and well-controlled indoor environment can enhance productivity among building occupants, leading to better work or living experiences.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: BAS often includes remote access capabilities, enabling building managers to monitor and control building systems from anywhere, enhancing operational efficiency and convenience.
- Predictive Maintenance: BAS can monitor equipment health and performance, detecting potential issues before they cause major problems. This proactive approach to maintenance minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of building systems.
- Improved Security: Integrating security features like access control, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems enhances building safety and provides a higher level of security for occupants and assets.
- Sustainability: Building automation promotes sustainable practices by reducing energy waste and contributing to green building initiatives and certifications.
- Real-time Analytics: BAS can gather and analyze data from various sensors, providing insights into building performance and helping identify areas for improvement and optimization.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Building automation systems are designed to be flexible and scalable, allowing easy integration with new technologies and expanding as building needs change.
- Compliance and Reporting: BAS can facilitate compliance with environmental regulations and building codes while providing detailed reports on energy usage and environmental performance.
- Faster Response to Emergencies: Incorporating fire safety and security systems into the BAS allows for quicker response times to emergencies, enhancing the safety of building occupants.
Overall, building automation systems create smarter and more efficient buildings, offering numerous benefits that enhance comfort, save resources, and contribute to a sustainable and well-maintained environment.
How does the building automation system work?
Building automation systems (BAS) use advanced technology to control and monitor various building functions, such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, security, and more. These systems are designed to improve energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and overall building performance.
BAS works by integrating various sensors, controllers, and actuators throughout the building. Here’s a simplified overview of how it functions:
1. Sensors: BAS includes different sensors like temperature, humidity, occupancy, light level, etc. These sensors continuously collect data about the building’s environment.

2. Controllers: The collected data is sent to central controllers, which are essentially the brains of the BAS. The controllers process the information and make decisions based on predefined algorithms and set points.

3. Actuators: Based on the decisions made by the controllers, actuators are activated to adjust building systems. For example, turning on or off HVAC systems, adjusting lighting levels, opening or closing blinds, etc.

4. Communication: The controllers communicate with the various building systems and components through wired or wireless connections. This enables seamless coordination and control of different functions.

5. Monitoring and Optimization: BAS continuously monitors the building’s performance, energy usage, and environmental conditions. It can automatically adjust settings to optimize energy efficiency and comfort, based on real-time data.

6. User Interface: BAS typically offers a user-friendly interface (such as a computer program or mobile app) that allows building managers or occupants to monitor and control the system manually if needed.
By automating and optimizing building operations, BAS can lead to significant energy savings, reduced maintenance costs, and improved occupant comfort. It also plays a crucial role in smart buildings and sustainable construction practices.
Applications of building automation system
Building Automation Systems (BAS) have numerous applications across various types of buildings. Here are some specific applications:
- Commercial Buildings: BAS is widely used in office buildings, shopping malls, hotels, and other commercial spaces to control HVAC, lighting, and security systems, leading to energy savings and improved occupant comfort.
- Industrial Facilities: BAS is essential in factories and manufacturing plants to monitor and control complex industrial processes, optimize energy usage, and ensure safety compliance.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: In medical settings, BAS helps maintain precise temperature and humidity levels, regulates air quality, and controls critical systems like medical gas supply and operating room environments.
- Educational Institutions: BAS is used in schools and universities to manage energy consumption in classrooms, libraries, and administrative areas, thus contributing to sustainability efforts and budget savings.
- Data Centers: BAS helps maintain precise environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to safeguard sensitive equipment and ensure data center efficiency.
- Residential Buildings: In modern homes, BAS can control lighting, HVAC, and other systems, offering homeowners convenience, energy savings, and the ability to monitor their property remotely.
- Retail Spaces: BAS optimizes energy usage in stores by controlling lighting and HVAC based on foot traffic and business hours, thus reducing operating costs.
- Hospitality Industry: BAS is employed in hotels and resorts to manage room climate, lighting, and other services, providing guests with a comfortable and personalized experience.
- Airports: In airports, BAS controls lighting, ventilation, and escalators based on passenger flow and schedule, ensuring efficient operations and energy management.
- Entertainment Venues: BAS is utilized in stadiums, theaters, and concert halls to regulate indoor climate and lighting, enhancing the overall visitor experience.
- Laboratories: In research facilities and laboratories, BAS ensures strict control over environmental conditions to support precise experiments and protect sensitive equipment.

Building automation system in India
The demand for building automation systems in India is on the rise due to several factors. With rapid urbanization and a growing population, there is an increased need for efficient and sustainable building solutions. Building automation systems offer a range of benefits such as energy efficiency, cost savings, enhanced security, and improved occupant comfort.
As businesses and industries in India focus on optimizing their operations, building automation systems become a crucial tool to streamline and manage various building functions. The rise of smart cities and the government’s push towards sustainable infrastructure also contribute to the increasing demand for automation systems in buildings.
Furthermore, the adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) technology in the construction industry is driving the integration of smart devices and sensors, making buildings smarter and more interconnected. This, in turn, fuels the demand for building automation systems as a means to centralize control and monitoring.
Conclusion
Building automation systems have become indispensable tools for creating smarter, greener, and more responsive buildings. With continuous advancements and a strong focus on security, these systems are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable and intelligent urban environments. Embracing bui

