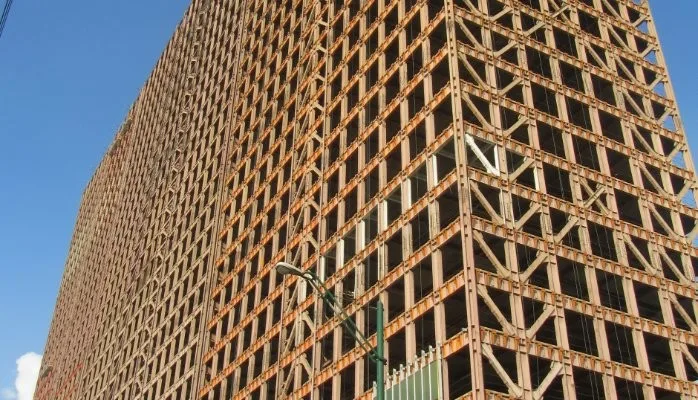
A tubular structural system is used in high rise buildings that utilises hollow tubes, often made of materials like steel, aluminium and composite materials. These tubes serve as columns and beams, providing essential vertical and horizontal support. This type of structural system enhances the structure’s strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to buckling, and seismic performance. Tubular members are usually prefabricated off-site, enabling efficient on-site assembly, thereby expediting construction and potentially reducing costs.
Historical Significance
Fazlur Rahman Khan, widely acknowledged as the father of tubular design in structural engineering, introduced this groundbreaking system. The DeWitt Chestnut Apartment Building in Chicago, developed by Khan in 1963, stands as the inaugural tube-frame structure, marking a pivotal moment in architectural innovation.
Structural configuration of tubular structural system
In this type of structural system the primary load-bearing elements, such as columns and perimeter walls, are arranged to form a tubular shape. This configuration helps in distributing structural loads more efficiently, providing stability and resistance against lateral forces like wind and seismic activity. The tube system is particularly effective in tall structures as it minimises the need for extensive internal columns, allowing for open floor plans and maximising usable space.
The arrangement of tubular structural systems
The arrangement of a tubular structural system depends on the specific design and architectural requirements, but commonly involves the following principles:
1. Core Structure: A central core, often housing elevators, stairs, and services, forms the primary load-bearing element. This core is typically a tube or a cluster of tubes, providing vertical support and stability.
2. Perimeter Columns or Braces: External tubes or columns surround the perimeter of the building, forming a protective shell. These elements help distribute lateral loads, such as wind or seismic forces, and contribute to the overall stability of the structure.
3. Floor Diaphragms: Horizontal floor structures, also known as diaphragms, connect the core and perimeter elements. These diaphragms help in the distribution of loads horizontally and contribute to the overall stiffness of the structure.
4. Connection Systems: The connections between the core, perimeter, and floor elements are crucial for transferring forces efficiently. Welded or bolted connections are commonly used to ensure the integrity of the entire tubular system.
5. Trusses or Beams: In some designs, trusses or beams may be incorporated to provide additional support or to span large distances between columns. These elements can enhance the overall structural performance.
6. Facade Elements: The exterior of the building is often designed with aesthetic considerations in mind. The facade elements may follow the tubular pattern, creating a visually appealing and functional outer shell.
7. Interior Layout: The arrangement of interior spaces is planned around the core structure. The placement of rooms, partitions, and utilities should complement the overall stability and functionality of the tubular system.
The specific arrangement can vary based on the architectural vision, structural engineering requirements, and the intended purpose of the building.
Why is the tubular structural system used in high rise buildings?
- Distribute loads efficiently, allowing for the transfer of forces throughout the structure.
- Provide high strength and stability, particularly against compressive and torsional forces.
- Efficient material usage, optimising the structural integrity while minimizing weight.
- Less prone to buckling, enhancing their performance under different loading conditions.
- Contribute to aesthetically pleasing designs, offering both functionality and visual appeal.
- Straightforward construction leading to cost-effective and timely projects.
- Can be designed with various patterns and shapes, offering aesthetic appeal.
- Can dissipate seismic forces and prevent progressive collapse.
- Well-suited to handle wind loads, reducing the need for additional bracing.
Types of tubular structural system used in high rise buildings
1. Framed Tube Structural System:
The Framed Tube Structural System is characterised by closely spaced exterior columns intricately connected with deep spandrel beams. These beams, running continuously across each facade and building corners, enhance the overall stiffness of the structure. Comprising interconnected frames, braced frames, or shear walls, this system forms three-dimensional space structures. The interconnected elements create a vertical tube-like system effectively resisting lateral forces in any direction. This system is suitable for various floor plan shapes such as square, circular, rectangular, and freeform. This system efficiently supports buildings ranging from 38 to 300 metres in height.
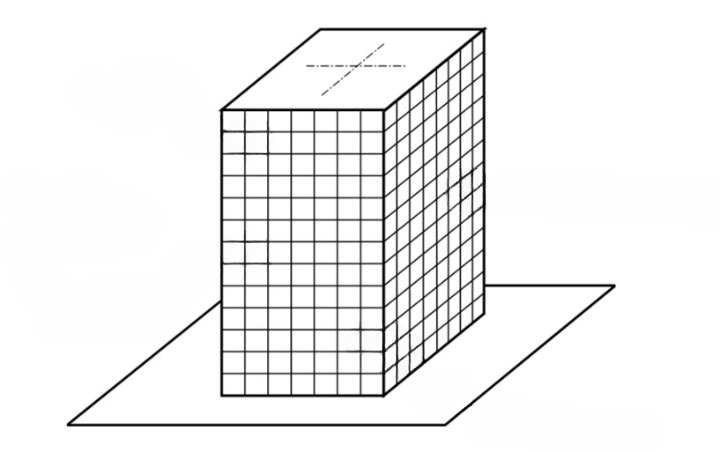
2. Trussed Tube System:
Trussed Tube Systems, also known as braced tube systems, share similarities with framed tube systems but with fewer external columns spaced farther apart. Incorporating steel bracing or concrete shear walls, this design creates a rigid box capable of resisting lateral shear through axial force in members. The wider column spacing allows for more precise areas for windows, making it an effective solution for high-rise buildings to withstand lateral loads like wind and seismic forces.
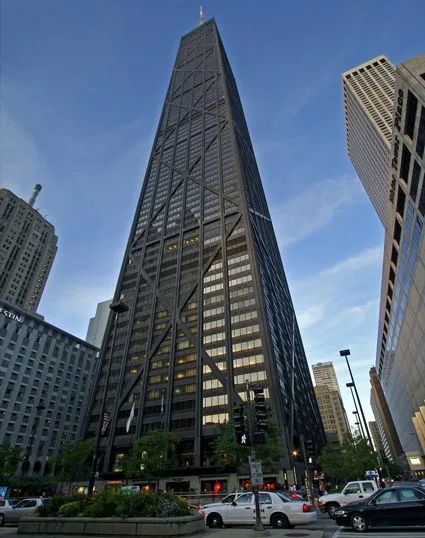

3. Tube-in-Tube Structural System:
The Tube-in-Tube Structural System, often referred to as the “hull and core” format, involves wrapping an external tube around a core tube. The core tube houses essential components like lifts, ducts, and stairs, while the external tube handles gravity and lateral loads. Interaction between the internal and external tubes creates shear and flexural branches, making it a versatile solution.
4. Bundled Tube Structural System:
The Bundled Tube Structural System comprises multiple connected tubes assembled to create a multi-cell tube. This collective arrangement enables the structure to withstand lateral loads and overturning moments effectively. Considered a cost-effective and versatile building system the tube-in-tube system allows for the creation of interesting shapes.
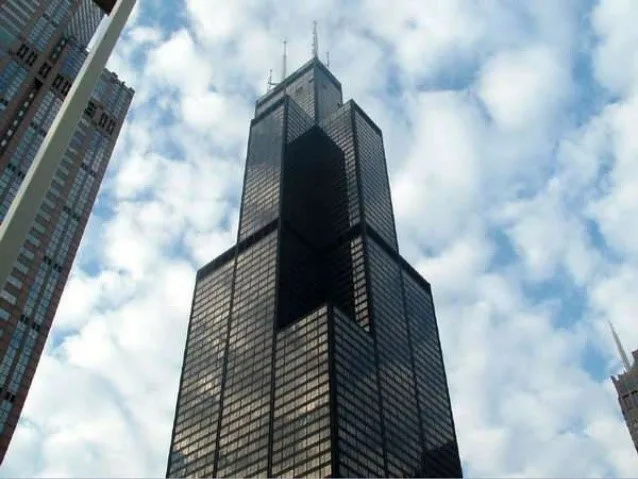

5. Hybrid Tube Structural System:
The Hybrid Tube Structural System comes into play when a building design requires a combination of structural forms for enhanced strength and stiffness. Common in complex structures, it integrates two or more structural forms in different parts of the building. This hybridization is essential when dealing with varying slenderness or strength requirements. Overall, the hybrid tube structural system exemplifies adaptability in addressing diverse challenges posed by complex building designs.
How to select the right tubular structural system used in high rise buildings?
- Choose a tubular system based on the height of the building.
- Assess the expected loads on the structure, including wind, seismic, and live loads.
- For seismic-prone areas, select the type known for good seismic performance.
- Choose a system that aligns with the desired architectural aesthetics.
- Opt for materials and designs that minimise environmental impact.
- Engage with experienced structural engineers to analyse the project requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, the tubular structural system emerges as a paramount choice for high-rise buildings, seamlessly combining robust engineering with architectural innovation. Its inherent strength, efficient load distribution, and design flexibility have revolutionised the construction of high rise buildings worldwide. Not only does this system meet the structural demands of but it also addresses contemporary concerns such as sustainability and rapid construction. As a symbol of engineering prowess and design finesse, the tubular structural system continues to redefine the skyline across the world.





