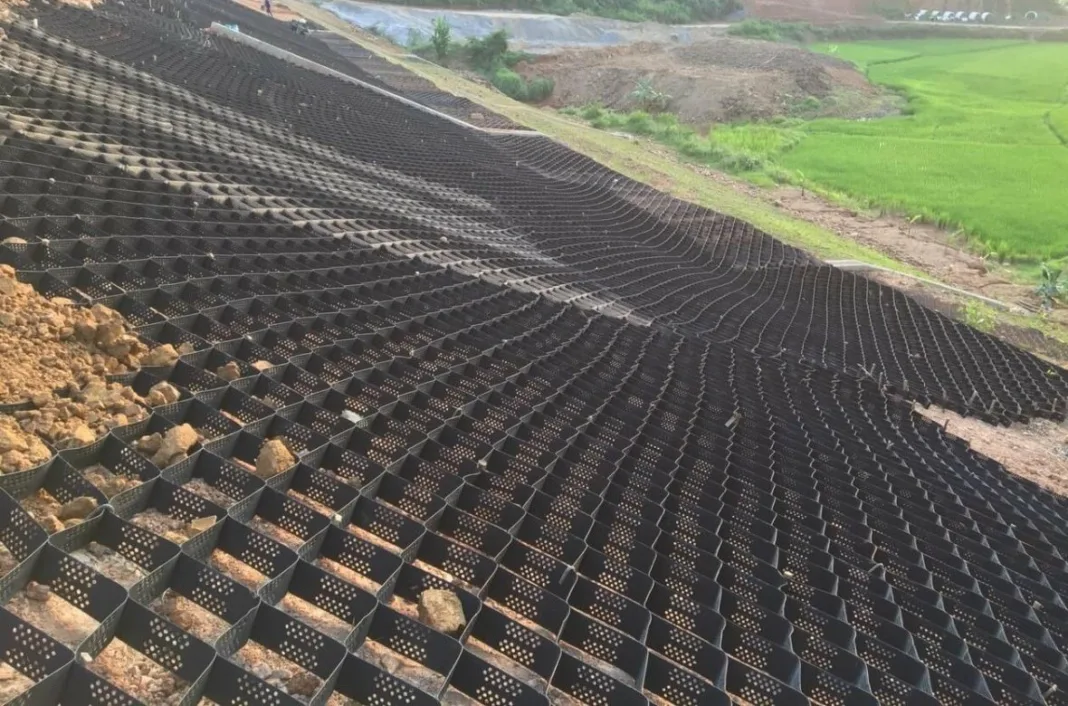
Geocells are three-dimensional structures from durable polymer materials, designed to enhance soil stability and prevent erosion. By confining soil or aggregate within their interconnected cells, geocells effectively reduce surface runoff and soil erosion, making them ideal for stabilising slopes and preventing landslides. Their unique design allows for the distribution of loads over a larger area, which not only increases slope stability and resistance to shear stress but also significantly aids in erosion control.
Geocells have a wide range of application areas, including:
- Road Construction
- Slopes
- Embankments
- Riverbanks
- Shorelines
- Hillsides
- Retaining Walls:
- Landfill and Reservoir
- Channel and Drainage Ditch
Advantages of geocells
- Enhances soil stability and prevents erosion effectively.
- Reduces surface runoff and controls sediment displacement.
- Increases load-bearing capacity in weak soils.
- Provides long-term durability and resistance to weathering.
- Minimises the need for heavy earthworks or excavation.
- Distributed loads evenly, reducing stress on subgrades.
- Suitable for use in various soil types and environmental conditions.
- Lightweight and easy to transport, handle, and install.
- Reduces construction and maintenance costs.
- Eco-friendly solution with minimal environmental impact.
- Improves safety by preventing slope failures and landslides
- Minimises disruption to surrounding ecosystems during installation.
Types of geocells
1. Polyethylene (HDPE) Geocells
Polyethylene (HDPE) geocells are widely used in civil engineering due to their durability and flexibility. Made from high-density polyethylene, these geocells are known for their resistance to UV degradation, chemicals, and environmental stress cracking. Their lightweight nature allows for easy handling and installation, even in challenging environments.They provide excellent load distribution, making them ideal for use in areas with soft soils or where heavy traffic is expected. Their strength and long-term durability make them a reliable choice for projects that require robust soil confinement and stability over time.
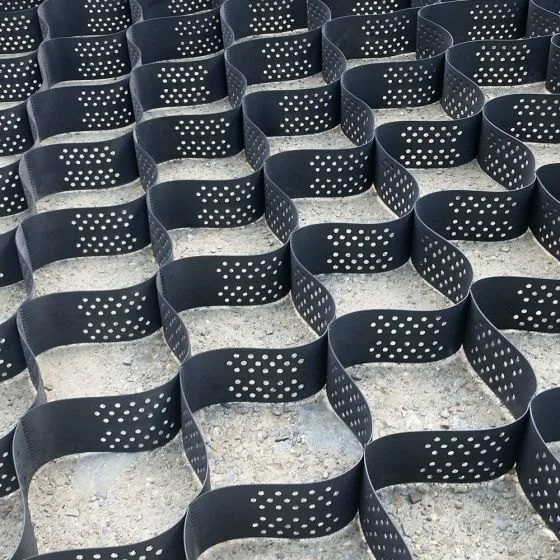

2. Polypropylene (PP) Geocells
Polypropylene geocells are lightweight and chemically resistant, offering flexibility that simplifies installation. They resist biological and chemical degradation, making them suitable for environments exposed to industrial chemicals or waste. Ideal for drainage applications like landfills, they excel in managing water. Their flexibility also allows for effective contouring on uneven surfaces, aiding in the stabilisation of slopes and embankments in challenging terrain.
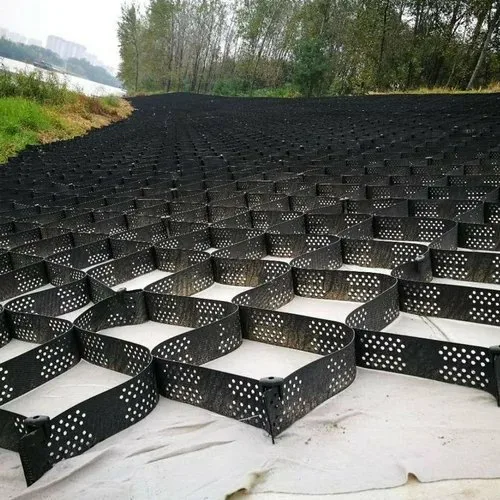

3. Textured Geocells
Textured geocells are designed with a rough surface to enhance the interlocking capability between the fill material and the geocell walls. This increased friction provides additional stability to the structure, reducing the risk of soil or aggregate movement within the cells. Textured geocells are particularly effective in areas where steep gradients pose a risk of soil erosion or landslides. The enhanced grip of textured geocells ensures that the fill material remains securely in place, making them an excellent choice for projects that require additional stability in steep or unstable environments.
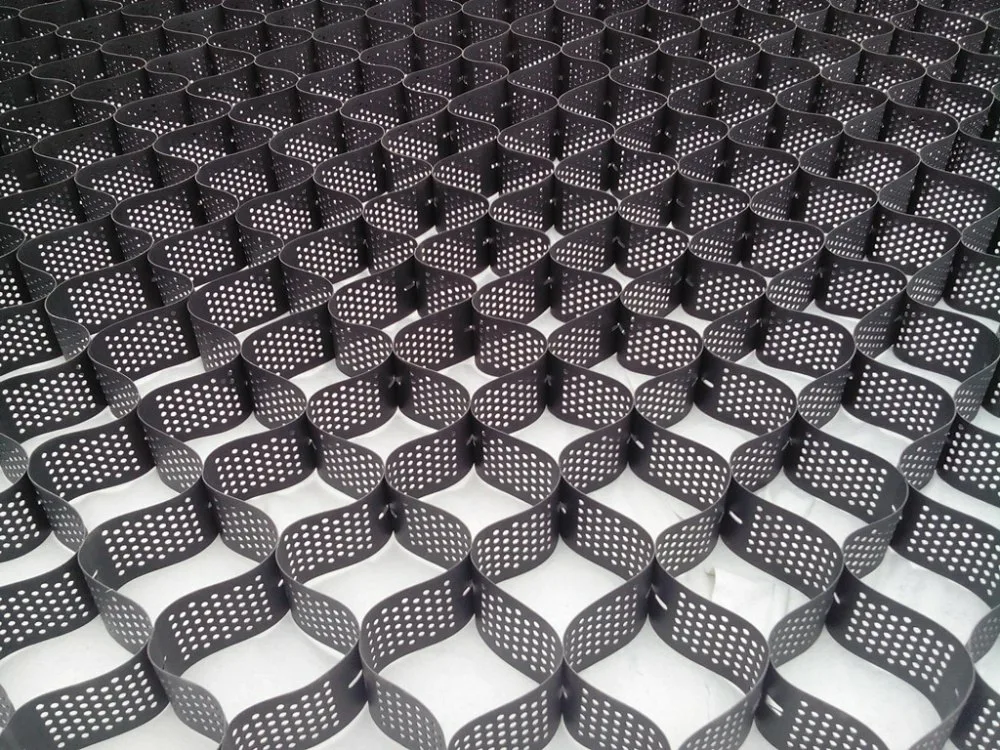
4. Perforated Geocells
Perforated geocells feature small holes along their walls, allowing for better water drainage and root penetration. This design makes them particularly suitable for projects where water management and vegetation growth are essential, such as in vegetated slopes or channels. The perforations prevent waterlogging, reduce soil erosion, and promote healthy plant growth, making them an environmentally friendly option. Perforated geocells are commonly used in green infrastructure projects, where aesthetics and ecological sustainability are key concerns. Their ability to allow for both structural stability and natural processes makes them a versatile solution for a range of applications.
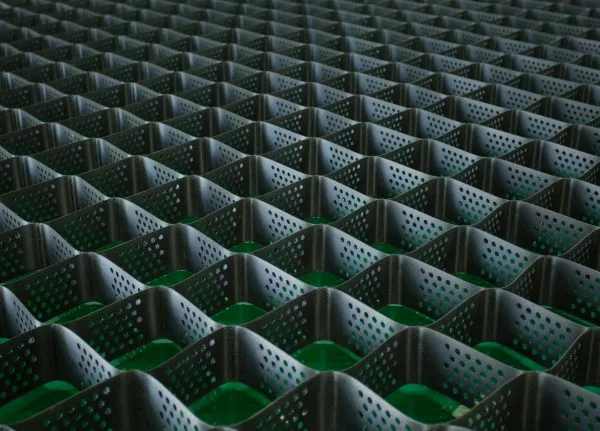
5. Non-perforated Geocells
Non-perforated geocells, as the name suggests, have solid walls without any holes, offering a more rigid and impermeable structure. These geocells are ideal for load-bearing applications where the primary concern is soil stabilisation rather than water management. They provide superior strength for supporting heavy loads, making them a popular choice for road bases, airfields, and other infrastructure projects where stability and load distribution are critical. Non-perforated geocells are particularly useful in environments where drainage is not required, and the focus is on providing strong containment and minimising soil displacement.
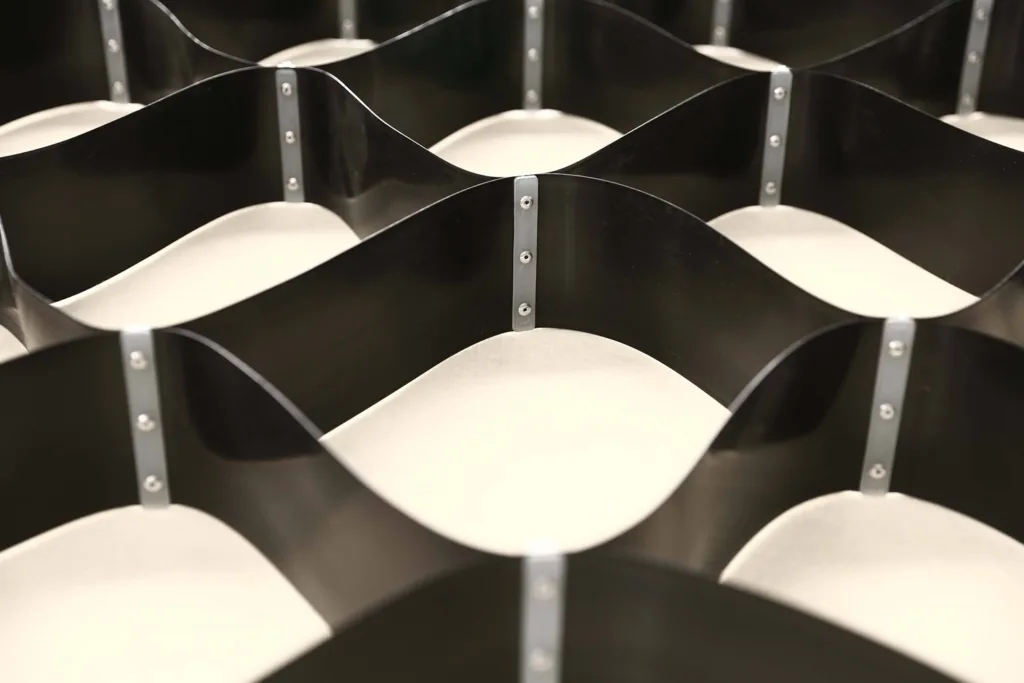

6. Composite Geocells
Composite geocells combine traditional geocell structures with additional layers, such as geotextiles or geomembranes, to improve performance in specific applications. These added layers can provide enhanced drainage, filtration, or waterproofing, depending on the project’s requirements. Composite geocells are often used in challenging environments, such as landfills or water reservoirs, where both structural support and environmental protection are needed.
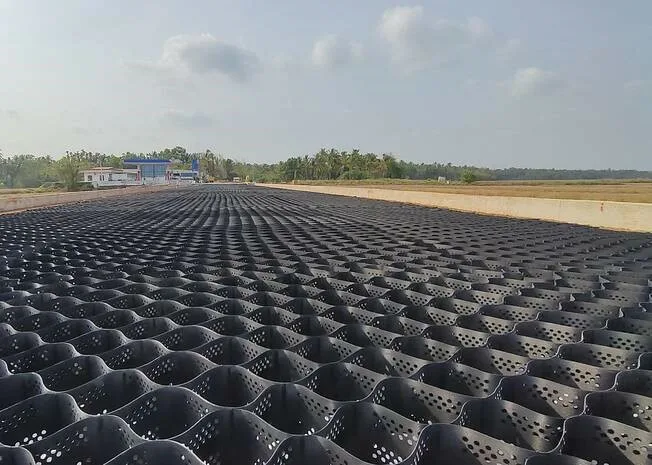

How to select the right geocell for your project?
- Assess the expected load to determine geocell strength.
- Analyse soil type, moisture content, and compaction needs.
- Consider exposure to UV, chemicals, and biological elements.
- Identify whether drainage or water retention is necessary.
- Evaluate site accessibility and ease of installation.
- Factor in cost-effectiveness, including material and labour costs.
- Consider the geocell’s lifespan and resistance to wear.
Application method of geocells
- Site Preparation: Clear the area of debris and level the surface.
- Base Layer Installation: Place a geotextile or aggregate base if required to create a stable foundation.
- Geocell Placement: Expand the geocell panels and secure them to the ground using stakes or anchors.
- Filling the Cells: Fill the geocells with suitable material, such as soil, gravel, or concrete, ensuring even distribution.
- Compaction: Compact the fill material within the geocells to increase stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Final Layer: Add a top layer if needed, like gravel or asphalt.
- Inspection and Finishing: Ensure all geocells are properly aligned, filled, and compacted.
Conclusion
Geocells are versatile geosynthetic products used for erosion control and slope stabilisation. Their ease of installation makes them essential for managing challenging terrain and protecting natural landscapes in various infrastructure and environmental projects. As the need for resilient and sustainable infrastructure grows, geocells will continue to play an important role in driving effective and eco-friendly engineering solutions.





