Pedestrian mitigation measures are now needed the most. Several Indian cities have seen the decline in the quality of life of the residents as a result of the frequent traffic congestion, high accident rates, air pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions due to widespread usage of motor vehicles. The most common solution adopted to address these issues is to increase road capacity in order to reduce the negative externalities associated with the increase in usage of motor vehicles.
However, research and international consensus increasingly point to this as a short-term solution that only temporarily eases traffic flow while also stimulating an increase in vehicle ownership and use, which will lead to more of the same problems going forward in the future. Therefore, managing the demand and supply for transportation in a holistic manner could be a superior strategy for developing sustainable urban transportation systems that enable people and goods to move without affecting the quality of the life of the urban residents.
Present Scenario of Mode share in India:
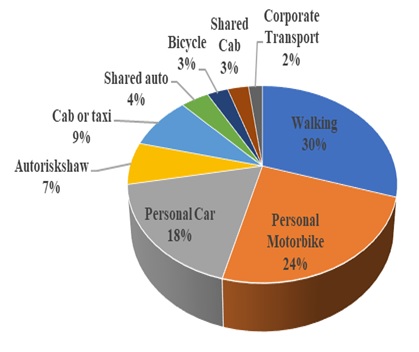
The statistics retrieved from the report published by Soman et al. (2019), on urban travel and commuting characteristics in India’s tier-1 and tier-2 cities revealed that walking is the most extensively used means of transportation, followed by personal motorbikes. Walking is an essential aspect of the transportation network because it is required to start and end almost every journey. Walking is considered as the primary mode of transport, especially for the shorter travel duration.
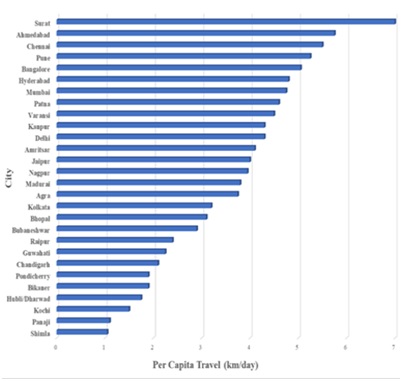
Walking is also an essential mode to support the public transport systems, improving the overall livability of the city, providing accessibility within built areas, and providing an alternative to private vehicles for short-distance trips. Short-distance trips are common in Indian cities characterized by very high population densities and mixed land-use development. As walking is an important mode, with estimated mode share value of around 30%, a report published by Asian Development Bank in 2009 revealed that the per capita travel length of the pedestrians is ranging from around 1 km/day in Shimla to around 7 km/day in Surat city (ADB, 2009). However, the conventional land-use and transit planning approach in Indian cities still pays little consideration to walking.
Issues with the Pedestrian Facilities in Urban India and need of Pedestrian mitigation measures
In spite of having a significant mode share and travel length, there is no strict provision for providing the necessary pedestrian mitigation to provide a safe walking environment for the pedestrians. As per the reports, pedestrians accounted for 14% of all road deaths in India (Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, 2019). Hence, pedestrians are the most vulnerable road users, and their safety has to be at the highest priority. As a result of being a particularly susceptible road user. Pedestrian deaths mainly can be traced to pedestrians walking along the roads. There are a variety of reasons why a pedestrian would choose to walk on the road, increasing the risk of colliding with a vehicle.
- Lack of Dedicated Sidewalks for Pedestrians
A sidewalk is a paved pedestrian walkway that is built parallel to the road. In general, they are referred to as footpaths. Due to a lack of dedicated sidewalks, pedestrians often walk on the shoulders. As a result, pedestrians travelling along such road lengths are more likely to be engaged in an accident with moving motor vehicles.

- Encroachment of the Sidewalk
An encroachment is a physical trespass into the area designated for pedestrian movement on the sidewalks. In general, shops in commercial areas take advantage of weaker legal enforcement by encroaching on sidewalk spaces and using them as part of their business area. Due to such encroachments would drive people onto the roads.

- Lack of Maintenance of Sidewalks
The term maintenance can be referred to both repair of damaged portions and cleaning of the sidewalk to maintain its aesthetic appearance. Cleaning refers to the removal of litter, animal waste, and debris from sidewalks. It is common practice to construct sidewalks when constructing a new road, and regular maintenance such as repair and cleaning is usually neglected, resulting in pedestrian’s reluctance to use sidewalks and are forced to stroll on the roads.

- Absence of dedicated Crosswalks
Crosswalks are usually characterized by zigzag lines on both sides and alternate black and white stripes on the road. In the Indian setting, such crossings are known as Zebra crossings. The zigzag lines serve as a warning to vehicles that pedestrians may be crossing or waiting to cross the road. They also inform drivers that they must yield to pedestrians crossing a road. The absence of dedicated crosswalks for crossing roads would increase the risk of pedestrians colliding with moving vehicles.

- Absence of Traffic Signs and Signals
A traffic signal is often installed to govern vehicle traffic passing through an intersection of two or more roads by visually indicating to drivers when they should proceed, slow down, or stop. Absence of such traffic signals to regulate the movement of vehicles and pedestrians at crossings, would increase the risk of accident between pedestrians and motor vehicles.

- Traffic Volume
Traffic volume is defined as the number of vehicles crossing a section of road per unit time at any selected period. It is reported that motor vehicles are growing at an exponential rate in India. The rising traffic volume is a biggest concern for the pedestrians, as it provides a limited time gap for the pedestrians to cross the roads, increasing the risk of collision between the vehicles and the pedestrians.

Possible Solutions:
The existing pedestrian mitigation measures must be adopted in order to improve the quality of life. As a green active mode, the promotion of walking would aid in the development of sustainable urban communities with the improved quality of life for urban commuters. Promoting walking as a primary mode of transportation offers numerous benefits, including reduced detrimental environmental impacts, increased personal mobility, and enhanced commuter health.
- Continuous Sidewalk
To accommodate pedestrians, wide and continuous sidewalks needs to be constructed. The presence of such continuous sidewalks would encourage commuters to walk for short and long distances. A proper design approach should be adopted to accommodate all the pedestrian demand generated along that route. To determine the actual demand of pedestrians, a survey related to pedestrian volume count should be conducted. The construction of a continuous sidewalk with adequate design standards would eliminate the need for pedestrians to walk on the streets, thereby minimizing pedestrian-motor vehicle collisions.

- Pedestrian Crosswalks Areas
The construction of such crosswalk areas would give a dedicated crosswalk area for pedestrians to safely cross the road. The presence of such crosswalk areas would also serve as a warning to drivers of motor vehicles to reduce their speed and stop before, allowing pedestrians to safely cross the roads. Therefore, construction of crosswalks should be assigned highest priority in terms of development across all relevant locations. Before construction, proper investigations must be carried out to establish specific crossing zones across busy routes. In the event of high pedestrian volume streets, the gap between crosswalks should be low, and in the case of low pedestrian volume streets, the interval can be increased.

- Traffic Signal and Signs
The traffic signs, which are normally installed on the side of a roadway and have a distinctive design, display symbols or words of warning or instruction to pedestrians and the drivers. The installation of such traffic signs would alert pedestrians to the presence of crosswalks and even alert drivers of motor vehicles to the presence of pedestrian crossings.

- Foot over bridges
Foot over bridges are narrow bridges that are normally built to allow people to cross safely. A foot over bridge connects two sides of a main road, allowing pedestrians to cross without having to wait for vehicles to pass. They should be built across busy streets to allow pedestrians to safely cross without stopping or disrupting the movement of traffic.

- Guard Rails
Guardrails are a permanent physical barrier that should be built along the sidewalk’s borders to serve as a barrier between pedestrians and motor vehicles. Guard rails will also protect the sidewalks from being encroached upon. The pedestrians would feel safer with these guard rails.

- Roadside Amenities
Pedestrian amenities such as benches, street lighting, public restrooms, and trees should be provided across the sidewalks. These amenities significantly improve the attractiveness and convenience of the pedestrian environment, and will encourage a higher number of commuters to prefer walking for both short- and long-term travel. Because, the importance of walking times depends on the purpose of the pedestrians, as people also walk to spend time, not to save time; walking the additional distance may be pleasant for the pedestrians, especially in areas that are conducive for walking. As a result, appropriate consideration must be given to the provision of such amenities in order to have a positive impact on pedestrian movement.

In order to provide a sustainable walking environment, there is a need to improve the existing pedestrian mitigation measure all across the major roadways in Urban Indian settings. Pedestrian mitigation measures are the need of time.
Authored By:


All photos are taken by the authors for their project work on Pedestrian Infrastructure Evaluation in Hyderabad





