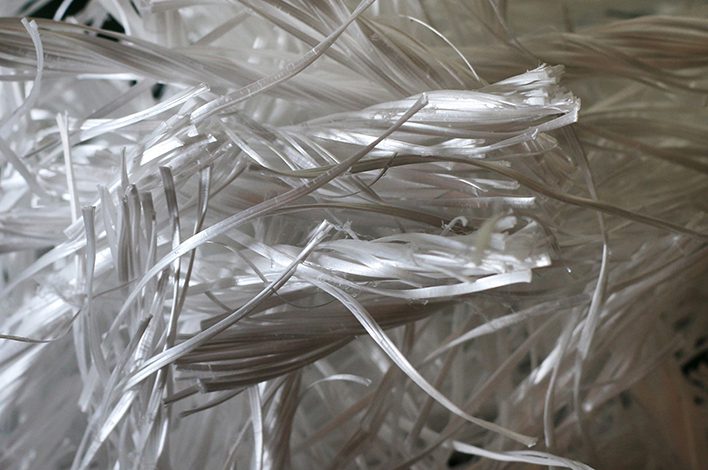
Fibre-reinforced materials are increasingly becoming a core component of precast and modular construction systems. With the industry shifting toward faster, factory-controlled building methods, fibres help enhance strength, durability, and performance while supporting efficient off-site manufacturing.
By integrating different types of fibres into concrete and composite elements, precast and modular structures achieve better crack control, load distribution, and long-term serviceability—making them ideal for modern infrastructure and building projects.
Applications of Fibre Reinforcement in Precast & Modular Construction
Fibre reinforcement is widely adopted across various precast and modular components to improve performance during manufacturing, transportation, and installation.
- Precast wall panels – Improves crack resistance, surface integrity, and handling strength
- Modular floor and roof slabs – Enhances flexural capacity and minimizes shrinkage cracking
- Facade and cladding panels – Enables lightweight, thin-section architectural elements
- Precast beams and columns – Increases toughness and load-bearing efficiency
- Tunnel linings and utility modules – Provides impact resistance and durability in aggressive environments
- Industrial and warehouse modules – Improves abrasion resistance under heavy usage
- Bathroom and kitchen pods – Ensures dimensional stability and reduced micro-cracks
- Precast pavements and pavers – Enhances fatigue resistance and service life
- Sandwich panels and GFRG systems – Improves composite action and structural reliability
- Temporary and relocatable structures – Supports lightweight yet strong modular systems
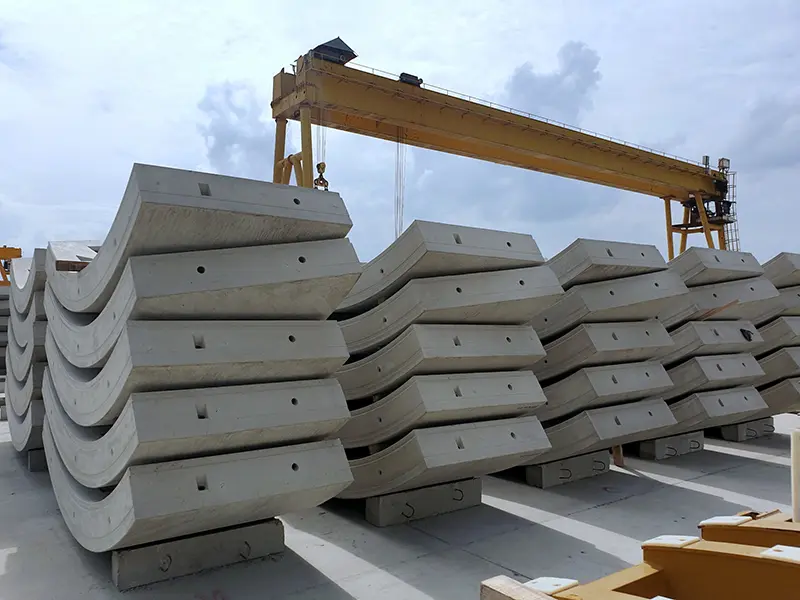

Advantages of Fibre Use in Precast & Modular Systems
The inclusion of fibres delivers both structural and operational benefits, making precast elements more resilient and efficient.
- Controls plastic and drying shrinkage cracks
- Improves tensile, flexural, and impact strength
- Reduces dependence on conventional steel reinforcement
- Enhances durability against corrosion and chemicals
- Improves fatigue and vibration resistance
- Enables thinner and lighter precast components
- Improves fire performance in specific fibre systems
- Enhances handling strength during transportation
- Accelerates factory production cycles
- Reduces long-term maintenance costs
- Enables complex architectural shapes
- Supports material efficiency and sustainability
Studies by the Fédération internationale du béton (fib) indicate that fibre-reinforced concrete can reduce crack widths by 40–60%, significantly improving durability in precast applications.
Types of Fibres Used in Precast & Modular Construction
Different fibre types are selected based on structural demands, exposure conditions, and design requirements.
Steel Fibres
Steel fibres provide high tensile strength and toughness, making them suitable for structural precast elements such as slabs, beams, and tunnel segments. They help improve load transfer and impact resistance while reducing crack propagation.
Glass Fibres (GFRC / GFRP)
Glass fibres are commonly used in architectural precast and façade panels. They enable thin, lightweight elements with excellent surface finishes and corrosion resistance.
Polypropylene Fibres
These synthetic fibres are effective in controlling plastic shrinkage cracks and improving surface durability. They are widely used in non-structural precast panels and modular floor systems.
Carbon Fibres
Carbon fibres offer exceptional tensile strength, low weight, and corrosion resistance. They are used in high-performance precast components where durability and weight reduction are critical.
Basalt Fibres
Basalt fibres provide good thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. They are increasingly adopted as a sustainable alternative to glass and steel fibres.
Fibre-Reinforced Concrete in Modular Construction
In modular construction, fibre reinforcement aligns perfectly with factory-based production methods. It reduces the need for traditional rebar placement, simplifies mould designs, and enables faster demoulding and higher production efficiency.
Fibre-reinforced modules also perform better during transportation and on-site assembly due to improved toughness and crack resistance.
According to MarketsandMarkets, The GFRC market is estimated at USD 2.01 Billion in 2018 and is projected to reach USD 3.32 Billion by 2023, at a CAGR of 10.5% between 2018 and 2023.
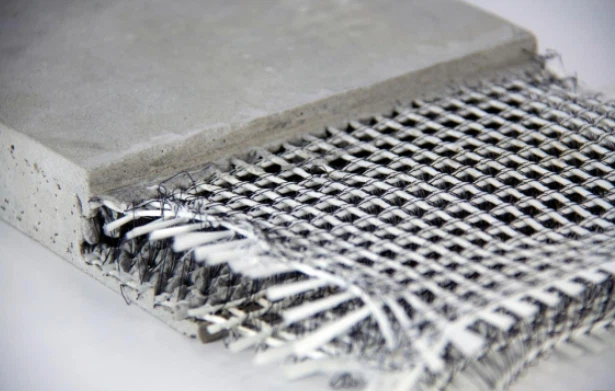
Sustainability and Performance Benefits
Beyond structural performance, fibre applications support sustainability goals by reducing steel consumption, minimizing material waste, and extending the lifecycle of precast elements. Lightweight fibre-reinforced components also reduce transportation emissions and improve overall energy efficiency in buildings.
These benefits make fibre reinforcement particularly valuable in large-scale modular housing, infrastructure, and industrial developments.
Conclusion
Fibre applications in precast and modular construction are reshaping modern building practices by combining strength, durability, and efficiency. From crack control and load enhancement to faster production and sustainability benefits, fibre-reinforced systems address many challenges associated with contemporary construction demands.
As off-site and prefabricated construction continues to grow, fibre reinforcement will remain a critical enabler of high-performance, resilient, and future-ready precast and modular structures.





