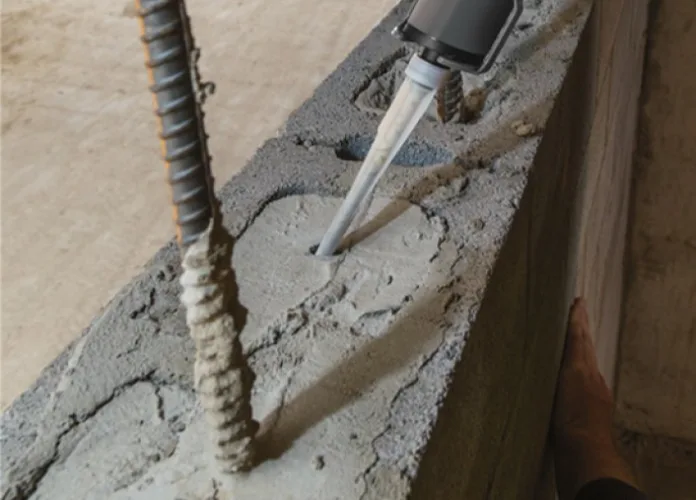
Epoxy adhesive chemical anchors are used for establishing robust and enduring bonds among structural elements. It consists of epoxy resin and a hardening agent. When mixed together, they react chemically form a strong adhesive that can securely bond materials together. These anchors are commonly used in construction to secure bolts, rods, and other fasteners in concrete, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity. Their ability to resist environmental factors, such as moisture and chemicals, makes epoxy adhesive anchors a reliable choice for important applications in building and infrastructure projects.
Advantages of epoxy adhesive anchors
- Provide a robust bond, ensuring a strong connection between materials.
- Suitable for various materials, including concrete, stone, and masonry.
- Resistant to environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and temperature.
- Provide effective vibration resistance for stability and safety.
- Quick curing times allow for faster construction processes.
- Capable of handling heavy loads in critical applications.
- Can be applied in confined spaces and overhead.
- Withstand exposure to various chemicals for stability in corrosive environments.
- Minimal shrinkage during curing, maintaining component integrity.
Types of epoxy adhesive anchors
1. Injectable Epoxy Anchors:
Injectable epoxy anchors offer versatility in bonding applications, involving the injection of a well-mixed epoxy compound into pre-drilled holes within diverse substrates like concrete or masonry. Known for their adaptability across various scenarios, these anchors provide a robust bond in intricate construction projects. The injection method ensures precise placement, making them particularly suitable for complex structures. Typically supplied in dual cartridges, injectable epoxy anchors facilitate accurate mixing during application, ensuring optimal effectiveness.

2. Capsule Epoxy Anchors:
Capsule epoxy anchors streamline the installation process with pre-measured capsules containing epoxy components. These capsules are broken open during installation, providing a controlled and convenient application. Noteworthy for their pre-measured design, capsule anchors simplify the mixing process, reducing the likelihood of errors during installation. This makes them well-suited for projects where precision is paramount. Available in various sizes, capsule anchors offer flexibility in selecting the right amount of epoxy for specific anchor sizes and project requirements.

3. Vinyl Ester Epoxy Anchors:
Vinyl ester epoxy anchors incorporate vinyl ester resin, imparting enhanced resistance to chemicals. They find utility in applications where high chemical resistance is a critical requirement. Excelling in environments exposed to corrosive substances, these anchors are ideal for projects in industrial settings or areas with aggressive chemical conditions. Their vinyl ester formulation ensures durability and resilience, providing a reliable bond in challenging chemical environments. The vinyl ester composition contributes to the adhesive’s robustness, ensuring dependable performance in demanding conditions.
4. Styrene-Free Epoxy Anchors:
Styrene-free epoxy anchors are specifically designed to mitigate environmental and health concerns associated with styrene emissions during installation, offering an eco-friendly alternative. Ideal for projects prioritizing reduced emissions and environmental impact, styrene-free epoxy anchors address health and safety concerns during installation. The absence of styrene does not compromise bonding strength, offering a responsible choice in construction applications. Styrene-free formulations maintain high bonding strength while aligning with environmental and health-conscious construction practices.
5. Fast-Curing Epoxy Anchors:
Fast-curing epoxy anchors are engineered for rapid setting and curing times, expediting project completion. Selected for time-sensitive projects, these anchors contribute to faster work progress due to their quick-setting formulations. Their rapid curing properties enhance overall project efficiency. Fast-curing epoxy anchors often come with specific application guidelines, requiring precise execution to harness their accelerated curing capabilities effectively.
6. High-Performance Epoxy Anchors:
High-performance epoxy anchors are formulated to meet the demands of challenging applications, delivering exceptional strength and durability. Suited for critical projects where structural integrity is paramount, these anchors offer reliable performance under heavy loads or in situations requiring superior bonding capabilities. High-performance formulations may incorporate advanced additives and resins to enhance strength, ensuring reliability in demanding construction sites. .
7. Threaded Rod Anchoring Epoxy:
Threaded rod anchoring epoxy is tailored for securely anchoring threaded rods into concrete or masonry surfaces, establishing robust connections. Essential for applications requiring threaded rods for structural support, this epoxy type ensures a strong bond between the threaded rod and the substrate. Threaded rod anchoring epoxy often includes corrosion-resistant properties, making it suitable for outdoor or exposed installations where environmental factors may affect the anchoring system.

8. Rebar Bonding Epoxy:
Rebar bonding epoxy is formulated to establish a secure bond between reinforcing bars (rebar) and concrete structures, enhancing overall structural integrity. Important for reinforcing concrete structures, this epoxy type increases load-bearing capacity and resistance to tension forces. It strengthens the concrete matrix, promoting longevity and stability in reinforced structures. Engineered to ensure a durable bond between the rebar and concrete, rebar bonding epoxy contributes to the longevity and stability of reinforced structures.
How to select the right epoxy adhesive anchor?
- Identify the specific anchoring needs (bolts, rods, rebar) for your project.
- Ensure the epoxy is suitable for the substrate material (concrete, masonry).
- Match the epoxy’s load-carrying capacity with the expected loads in your application.
- Consider resistance to chemicals, temperature, and outdoor exposure.
- Align the epoxy’s curing time with the project timeline.
- Assess resistance to chemicals if the environment requires it.
- Seek advice from structural engineers or construction professionals for complex projects.
Applications method of epoxy adhesive anchors
1. Surface Preparation:
- Ensure the substrate is clean, dry, and free from dust, grease, or contaminants.
- Remove loose particles and debris from the drilling area.
2. Drilling Holes:
- Drill holes into the substrate at the specified diameter and depth using a suitable drill bit.
- Follow project specifications and anchor design requirements.
3. Cleaning Holes:
- Thoroughly clean the drilled holes using a brush, compressed air, or other appropriate methods.
- Remove any remaining debris to ensure proper adhesion.
4. Inserting Anchors:
- Place the anchor into the drilled hole, ensuring it fits securely and reaches the specified embedment depth.
- Align the anchors according to the project layout.
5. Mixing Epoxy:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to mix the epoxy thoroughly.
- Use the recommended tools and proportions for accurate blending.
6. Filling Holes:
- Load the mixed epoxy into a dispensing tool or cartridge gun.
- Inject the epoxy into the drilled holes, ensuring complete coverage and avoiding air pockets.
7. Inserting Fasteners:
- Immediately insert the fasteners (bolts, rods, etc.) into the epoxy-filled holes while the adhesive is still in a liquid state.
- Follow the recommended insertion depth specified by the anchor design.
8. Curing Time:
- Allow the epoxy to cure undisturbed for the duration specified by the manufacturer.
- Ensure the curing environment meets the recommended conditions.
9. Quality Control:
- Conduct quality control checks, such as torque testing for threaded anchors.
- Verify that the anchors are securely set and meet project specifications.
10. Finishing:
- Once the epoxy has fully cured, trim any excess adhesive protruding from the drilled holes.
- Clean the surrounding area to achieve a finished and aesthetically pleasing result.
Application of epoxy adhesive anchors
- Structural Reinforcement: Bolts, rods, and rebar anchoring in concrete or masonry.
- Concrete Repair: Bonding and repairing damaged concrete elements.
- Seismic Retrofitting: Enhancing structures to withstand seismic forces.
- Facade Systems: Securing cladding and curtain walls for stability.
- Bridge Construction: Anchoring critical components in bridge structures.
- Tunneling: Anchoring support systems and bolts in tunnel construction.
- Railroad Infrastructure: Securing rail tracks, railings, and critical components.
- Precast Concrete Elements: Anchoring connections in precast elements.
- Highway: Anchoring guardrails, signage, and critical components.
- Water Treatment Facilities: Securing pipelines and structural elements.
- Industrial Facilities: Anchoring machinery and supporting structures.
- Commercial Buildings: Securing façades, signage, and structural elements.
- Residential Construction: Anchoring wall ties, securing foundations, and reinforcing connections.
Conclusion
Epoxy adhesive anchors play an important role in construction, providing robust bonding for structural elements. Their versatility, durability, and resistance to various environmental factors make them a preferred choice. As technology continues to advance, the application of epoxy anchors is likely to expand, contributing to safer and more resilient built environments.

