Concrete cover, in reinforced concrete, is the least distance between the surface of embedded reinforcement and the outer surface of the concrete (ACI 130). The concrete cover depth can be measured with a cover meter.
Why concrete cover is provided for the reinforcement?
- To protect the reinforcement bars from corrosion against the ingress of environmental agents, viz., chlorides, carbon di oxide, sulphates, moisture, oxygen and other aggressive gases and chemicals.
- To protect the reinforcement bars from fire
What is the preferred shape and strength of the cover blocks for Concrete Cover Reinforcement
The shape of the cover blocks could be cubical or cylindrical. The cover blocks should be such that they have the same strength, durability and porosity as that of the main concrete member.
What are the characteristics of a good cover block for Concrete Cover for Reinforcement?
- Should have low permeability
- Should be strong enough to take the load which gets transferred on them during concreting
- Should be wear resistant
- They should be dense
What are the recommended covers for the various exposure conditions as per IS: 456:2000for Concrete Cover Reinforcement?
| Exposure condition | Nominal concrete cover in mm not less than |
| Mild | 25 |
| Moderate | 30 |
| Severe | 45 |
| Very severe | 50 |
| Extreme | 75 |
However, for a longitudinal reinforcing bar in a column, nominal cover shall in any case not be less than 40 mm, or less than the diameter of such bar. In the case of columns of minimum dimension of 200 mm or under, whose reinforcing bars do not exceed 12 mm, a nominal cover of 25 mm.
What are the environmental factors causing corrosion to the reinforcement?
- Carbon di oxide
- Chlorides
What are the disadvantages in providing large cover for Concrete Cover for Reinforcement?
- Large cover depths (50–75 mm) are required to protect reinforcement against corrosion in aggressive environments, but thick cover leads to increased crack widths in reinforced concrete flexural members.
- Large crack-widths (greater than 0.3 mm) permit ingress of moisture and chemical attack to the concrete, resulting in possible corrosion of reinforcement and deterioration of concrete.
- Therefore, thick covers defeat the very purpose for which it is provided. There is a need for judicious balance of cover depth and crack width requirements.
What is the provision for nominal cover to meet specified period of fire resistance in IS: 456:2000?
Table 16A of IS 456:200 gives the provision for nominal cover to meet specified period of fire resistance.
How corrosion is initiated due to Carbon di oxidefor Concrete Cover Reinforcement?
Carbon di oxide diffuses into concrete and reacts with calcium hydroxide and reduces the pH value of the concrete to a value below 9. Once the pH of concrete drops below 9, the passive layer in the reinforcement steel is broken and paves the way for corrosion, provided oxygen and moisture necessary for the reactions of corrosion are present. This phenomenon is also known as carbonation.
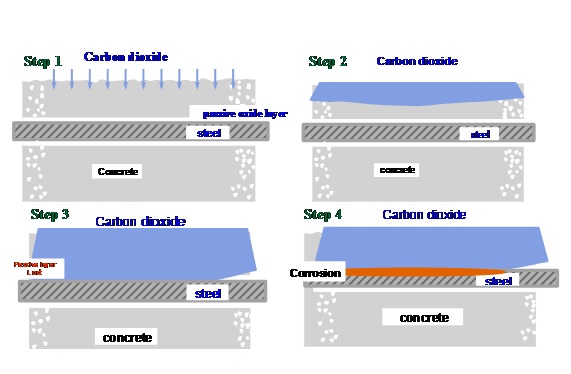
How corrosion is caused due to chlorides for Concrete Cover Reinforcement?
Chlorides diffuse into the concrete and break down the passive layer of steel, setting up alternate anodes and cathodes forming corrosion cells with concrete acting as an electrolyte. Once the passive layer of steel is broken, the corrosion of the steel reinforcement occurs in the presence of moisture and oxygen.


Conclusion
Cover blocks are provided to protect the reinforcement from corrosion and fire. Corrosion of reinforcement takes place due to diffusion of carbon di oxide and chlorides into concrete, which break the passive layer in the reinforcement steel. Quality of concrete in the cover region ultimately decides the durability and the service life of the structure.
Author

About Author – Author’s areas of research include Concrete Technology, Non- Destructive testing of RC structures and Repair and Rehabilitation of RC structures. He is involved in more than 150 consultancy projects for various Government, Public Sector and Private agencies, including Defense and Nuclear departments.





