Refrigeration is the heart of fish or shrimp processing plant. It all starts with the use of ice from the time of harvesting until it reaches to final consumer kitchen. It is highly necessary to keep the temperature chain intact to keep the quality of the product, whether it is fresh or frozen.
For a refrigeration plant to work efficiently it is really necessary to have a good processing plant layout. The simple reason is that every part inside the processing plant maintains a lesser temperature than the ambient temperature in most parts of the year. It means the building is energized, even more; appropriate to say that it is refrigerated. This is true for even those plants which do not have an air conditioning system inside the pre-processing and processing area. These areas are getting cooled by the energy given out by the melting of Ice.
Normally the plant design starts with a simple layout drawing. So the sizing of each process location is very important from the energy conservation point of view. The area should be well enough to process the required quantity. The additional area should be provided only if there is a requirement for future expansion. Not only the length and width but also the height of the processing area should be well enough to have more air space and good air ventilation. However, too high a process area will require more energy per unit area.

Before going to the equipment requirement in the plant let me explain the process area air conditioning requirements in the processing plant. The entire product handling area can be divided majorly into three portions, pre-processing, processing and packing area. It is required to maintain a minimum temperature of 22 to 24°C in all these portions. Another challenge in the industry is that the relative humidity in these areas goes above 95% due to heavy use of water and ice in the process. Over and above certain area near process refrigeration equipment, the air temperature goes below dew point temperature which condenses the moisture in the air. So it is necessary to maintain the above said temperature and bring down the RH level between 60 to 70%. A well designed air-conditioning system can directly give three benefits.
- Reduce melting of ice and heat gain by the product
- Reduce fatigue of the employees
- Eliminate unwanted condensation on surfaces especially on ceiling.

Just by providing cooling units may not serve the purpose. A very uniform and low velocity air-flow is required to meet all the above three mentioned requirements. Air distribution with textile socks system is the best method to achieve this. However, the cooling system should be well designed with proper heat load calculation.
Then coming to the selection of process equipment; the selection of every process equipment is highly important for efficient and hygienic operation. When we say efficient we need to look at,
- Energy Efficiency
- The efficiency with low product weight loss. (Freezing loss or Cooking loss)
Other indirect process equipment like water chillers and Ice making machines should also be efficient and more importantly it should meet the hygiene requirements. There are different types of water chillers like Shell and tube, Plate heat exchanger and Falling film. Since the process requirement calls for chill water temperature of 1 to 20c it is advisable to use a falling film chiller.
Similarly there are different types of ice being used in the industry. Block Ice, Tube Ice, Plate Ice and Flake Ice are commonly used. And each of them is produced in different types of machines/systems which produce ice in different shapes. Each one has its own advantages and disadvantages. Flake Ice is best rated for in-house process activities whereas crushed block ice is best rated to use long-distance transportation of raw material. But nowadays plate ice is finding its own space for both in-house use and raw material transportation due to its versatility in production to vary the thickness from 4 to 15mm thickness.

The most important process equipment in the industry is the IQF (Individual Quick Freezer) line and the selection of the machine is very tricky. Generally, we should look at the following factors to decide the selection,
- Freezing capacity per hour. Select the capacity which can best suit the material in feed capability. (Many times higher capacity freezers are selected but full utilization is never attained. At least 80% of the capacity should be achieved for the system to be energy efficient)
- The refrigeration load required to reach the production capacity.
- The evaporation temperature at which the refrigeration system to be designed.
- Having all accessories to suit best production practices.
- The major parts, the Freezer, Glazer and Hardener all should be well-designed equipment to avoid any clumps during production.

In the case of plate freezers the quality of plates, hoses, hydraulic systems are very important. In plate freezers often called contact freezers transfer the heat energy through contact and therefore the models with roll-up curtains will do the purpose instead of doors. Breaking of hoses or plate leaks is common defects found in the equipment especially units with low quality standards. So need to keep safety in mind while deciding on the ‘make’ of the unit.
Blast/tunnel freezers are commonly used in fish processing plants. This is a batch freezing process where the materials are generally loaded in a trolley and pushed into the blast freezer room for a specific time for freezing.
If the plant is having a cooking unit the cooking loss is the main criterion to be looked upon. Cooking with forced convection heat transfer understandably gives less cooking loss than conventional cooking methods.
Cold Storage Area
Above all the cold storage is the area where it is necessary to provide high priority during design. This is where final money is sitting. The cold storage consists of three sectors. The storage area, anteroom and the material dispatch area.
Commonly used material storage systems in the industry are,
- Mezzanine floor (Multi-tier flooring)
- Drive-in racking
- Single deep racking
- Double deep racking
- Mobile racking
- Pallet Shuttle system
1. Mezzanine floor (Multi-tier flooring)
This is a commonly used material storage system in most of the plants which are around 10 years and older. It has more disadvantages than advantages. First of all this is unsafe for human movement except on the ground floor. Other floors will get become slippery due to ice formation. It will be very difficult to locate the stored product unless a strict system of operation followed.

2. Drive-in racking
This type of storage racking is seen as being promoted extensively without clearly understanding the demerits. It is understandable when the racking has two or three deep and maximum of Ground plus three high. Whether it is two deep or three deep it will be advisable to use a double deep reach truck. However, there is no harm in going higher deep if the SKU (Stock keeping units) are two or three types.
But the seafood processing units have multiple SKUs. It has the only advantage of saving space nothing else.

3. Single deep racking
This is also known as selective racking. Though it is very good for the selectivity of material it occupies very large storage space. It requires more number of aisle that other storage racking design. Single deep racking system is seldom used in the industry.

4. Double deep racking
This can be rated as one of the best methods to be adopted in the industry. A double deep reach truck is used for material handling. It’s throughput will not be as good as single deep racking. But it well suits the industry. G+4 pallet height can be well optimized but can go even G+5 if the land is expensive and limited.

5. Mobile racking
The system is well suitable for chamber storage capacity greater than 1000 Pallet positions. A very high occupancy level is possible. This is a good system especially where the cost of the land is high. The risk is the high quality of floor construction requirements. It will be literally impossible to operate if the floor gets disturbed. The contraction or shrinkage on the floor can create a gap between rail and floor and start disturbing the movement of the rail. The throughput will be affected if storage is not organized. This is expensive compared to other racking methods.

6. Pallet Shuttle System
This is similar to drive-in racking but having special equipment called shuttle which moves on individual positions in depth. It requires multiple shuttles and reaches trucks if not the material throughput will be very slow. Not a very successful model for the industry.

Another area where proper attention is required is the anteroom. It should be provided with adequate space for movement of men and material. The best temperature to be maintained is +7°C to +10°C and should have ventilation of air to avoid condensation. Anteroom should have an effective air-lock system from the docking area. And the airlock should be well designed to ensure least fresh air intake which will reduce the infiltration load and moisture gain.

For the docking area the best method to load/unload material is by using a dock leveller which bridges the gap and height between the building and the vehicle. The height and position of the dock leveller should be well suitable for refrigerated trucks and container docking. Forklifts that are suitable for container loading can minimize the loading-unloading time very effectively.

Above all these points the design of the refrigeration plant is very crucial for energy-efficient operation. Ammonia is a very efficient refrigerant for this application. It’s safe when handled with care. The safety starts with the design, position of vessels, fabrication and testing of all vessels, selection of valves, welding of all joints, proper pressure and testing procedures, position of ammonia sensors, proper identification of pipes and proper air exhaust system for plant room and other critical areas. Proper safety equipment should also be available at the right place to handle an emergency situation. It is always advisable to keep the high-pressure receiver above the machine room or in a safe open place.
All standard compressors whether it is reciprocating or screw are efficient when taken individually. However, some of the compressors have oil lifting issues. This should be cross checked before selecting the compressor. Compressors driven with ‘Variable Frequency Drive’ by ensuring the speed variation in line with refrigeration capacity change will certainly ensure power saving. The speed variation with compressor capacity control in larger capacity compressors is the best combination to save the power. Evaporative condensers are the best type of condenser. Most of the evaporative condensers are with coil type heat exchangers and evaporative condensers with plate type heat exchangers are yet to get tested at various conditions.
Above all it is the system design that makes it efficient and effective. Selection of pipes, fittings, valves and controls in-line with the capacity requirement, velocity and pressure drop are very essential for a trouble-free system operation. All required safety devices and safety line components are must to safeguard operating equipment and human safety. Ammonia sensors at right place with alarms and system interlock are should not be avoided. The incorporation of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) will give immense benefit for the plant operation by making it simple at the same time very informative.
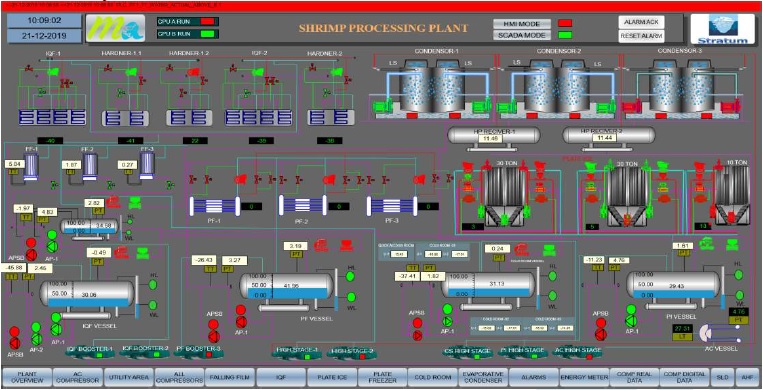
A designer and the owner should keep the above points in mind while planning for a new project or even an expansion. Even these thought process can be interlinked with the existing plant to make it better.
Authored By;
Sivakumar R Nair, Chief consultant – Stratum Project Consultants, Bangalore,
E-mail: siva@stratumpc.com, Mob: +91 99800 88268





