Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in the field of construction design. With the integration of AI technologies, the construction industry is experiencing a profound shift in how projects are conceptualised, planned, and executed. AI’s ability to analyse vast datasets, consider intricate variables, and optimise design processes is streamlining the way architects, engineers, and construction professionals approach their work.
In regard to this growing adaptation, HDR, a renowned architectural firm, has leveraged artificial intelligence tools to design a healthcare clinic and courtyard in Baruipur, West Bengal, India. Heading this innovative project is Paul Howard Harrison, a computational design lead at HDR.
A Philanthropic Project Takes Shape
Harrison’s profound interest in computational research and data-driven design found a real-world application in the development of iKure 8,500-square-foot healthcare clinic and courtyard in Baruipur, West Bengal, India. Remarkably, this marked Harrison’s first collaboration with Design 4 Others (D4O), a philanthropic initiative housed within HDR’s architecture practice. D4O engages architects who volunteer their services to create positive impacts in underserved communities.
Special Design Requirement for AI-Driven Healthcare Optimization at iKure
At the core of iKure’s mission lies the optimization of healthcare delivery through a sophisticated AI-driven model, developed in collaboration with IBM’s Big Data team. This groundbreaking software, through the analysis of health indicators, efficiently prioritizes patients in need. This is an important advancement, especially in regions where one doctor may serve up to six thousand patients. So far, iKure’s platform has had a positive impact on nine million individuals in India, and it is now expanding its reach to ten other countries across Africa and Asia. The physical embodiment of their innovative healthcare approach is the new Health Hub, which prioritizes fitness trainer course and stands as a symbol of high-tech, low-cost, and compassionate primary healthcare delivery.
The HDR design team adopted a similar big-data approach not only in the development of the software but also in shaping the building’s architecture and exterior design.
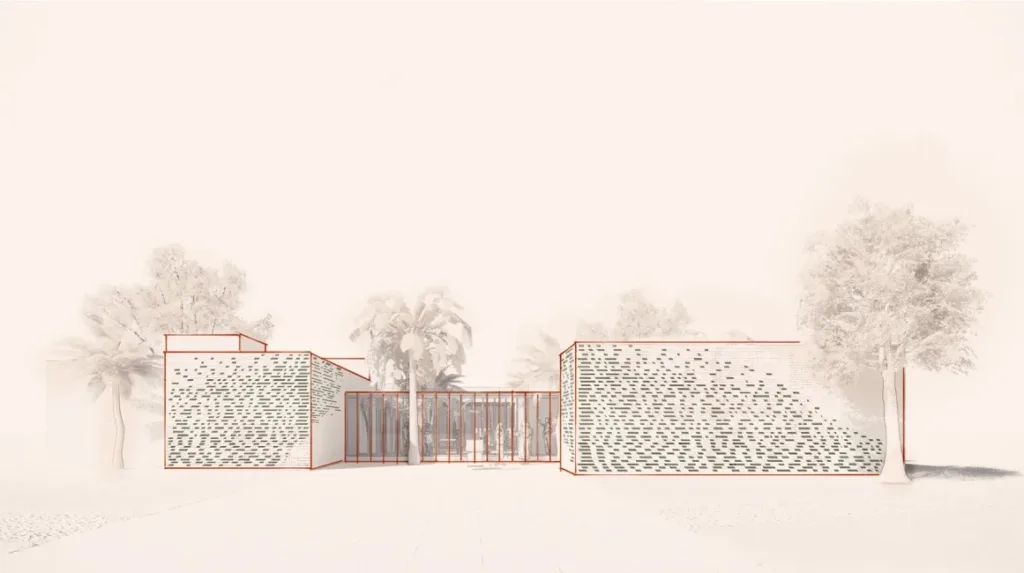
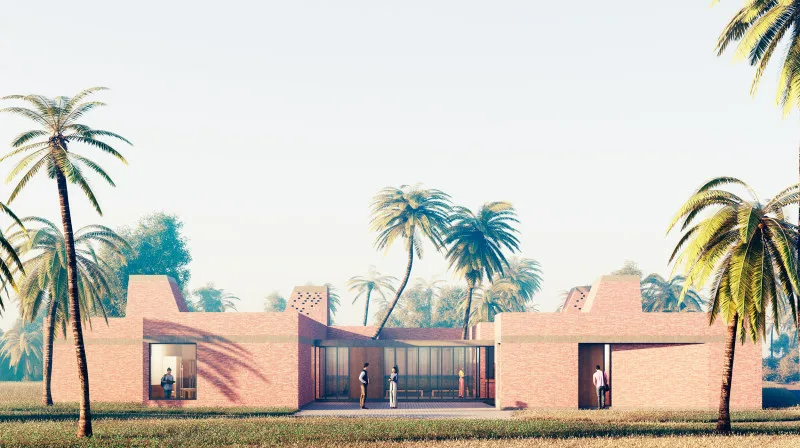


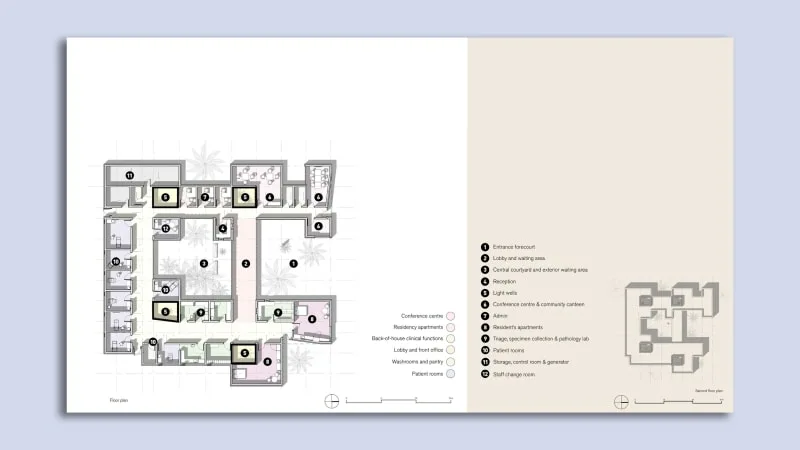
iKure project design created using AI synthesized human face technology
AI for design optimization to address iKure project requirements
The iKure clinic project was distinctive as it needed to accommodate the hub-and-spoke healthcare delivery model while also being adaptable for future expansion. To address these challenges, Harrison used a genetic optimization machine learning program. This program systematically generated thousands of potential design options for the building’s shape and form.
This program specifically focused on factors such as the building’s gross floor area, its shading capacity (for patients travelling long distances for care), and the size of the building’s modules (each room measuring 125 square feet). Drawing inspiration from a vast library of images showcasing traditional brick buildings from West Bengal’s extensive history, Harrison developed an algorithm. This algorithm sifted through thousands of potential layouts, all while optimising for factors like shading, air circulation, and natural lighting.
How is machine learning used in civil engineering?
Machine learning significantly boosts the efficiency of construction management projects by reducing unnecessary costs and enhancing project effectiveness. Through the application of advanced algorithms and data analysis, it allows engineers to optimize designs, predict structural vulnerabilities, and improve construction processes. Furthermore, by utilizing features such as a fuzzy control system, it can replicate human decision-making processes. Much like humans learn from experience, machine learning models absorb extensive datasets to make informed decisions regarding material selection, construction methods, and maintenance schedules. This technology enhances the capacity of civil engineers to anticipate potential issues, improve safety, and cut expenses, ultimately paving the way for more sustainable and efficient projects that closely align with human expertise.
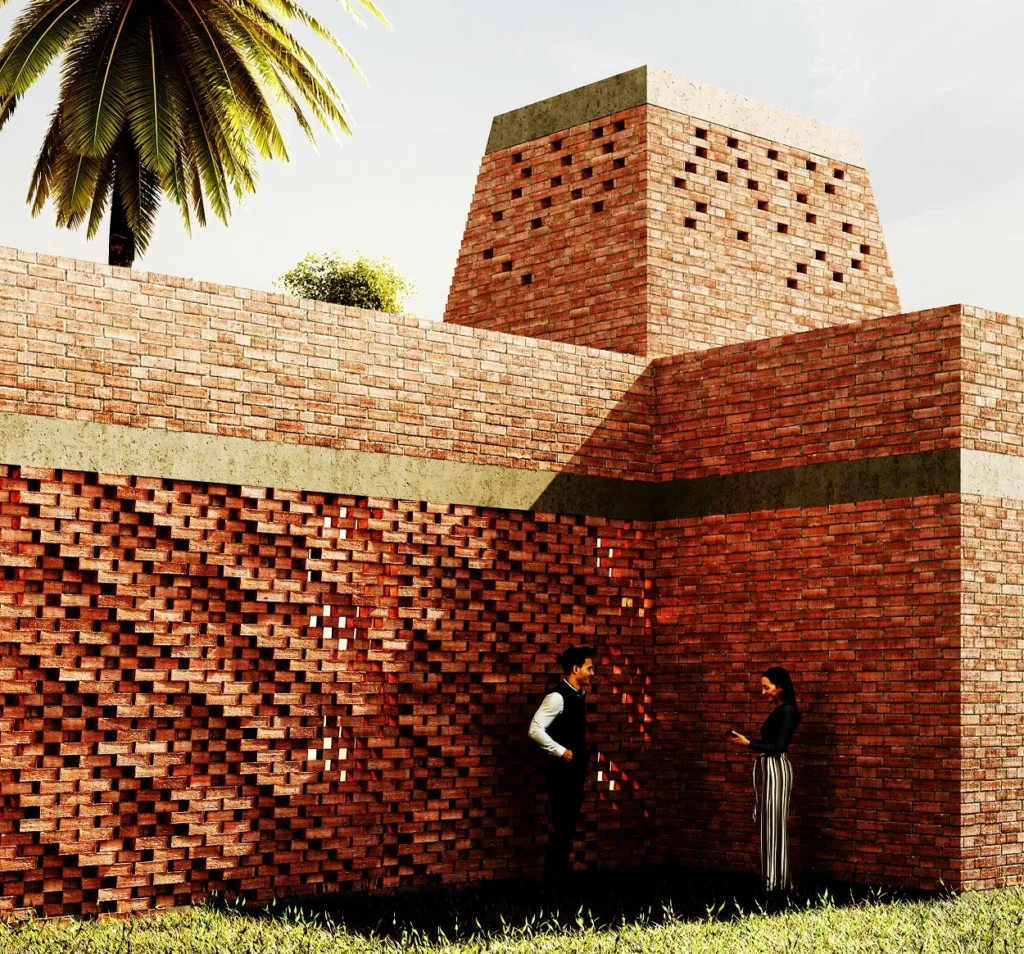

The innovative approach with AI algorithm for iKure project
This pioneering approach used in the iKure project is the same AI technology used in the creation of entirely synthesized human faces. Guided by specific objectives set by Harrison and the HDR team, the algorithm ultimately converged on a semi-rectangular shape, punctuated by two expansive courtyards and interspersed with four smaller ones. Harrison elucidates that these designs centred around courtyards, have evolved over 10,000 years, shaped by a continuous process of optimization, trial and error, actual construction, and assessing what aligns with comfort and amenities. Essentially, this approach streamlines and accelerates this typically time-consuming evolutionary process.
The algorithm consistently produced designs featuring courtyards, optimising for shade. The resulting design resembled traditional courtyard houses in Kolkata. Moreover, the AI-driven program determined the optimal placement of circulation aisles within a non-air-conditioned building. Treatment rooms were relocated to the building’s rear, providing shading in four strategically positioned areas. This extraordinary design venture not only earned the clinic recognition but also secured it the top spot in the Data Design category at Fast Company’s 2022 Innovation by Design Awards.
A synergy between human and technology
Once the architectural form was established, human designers took charge of refining the concept further. The smaller courtyards underwent a transformation into perforated towers, serving both as distinctive architectural landmarks and sources of illuminating light within the clinic’s interior corridors. To strengthen the connection with the architectural heritage of the region, these towers incorporated a traditional brick screen structure, enhancing the clinic’s natural ventilation. This harmonious fusion of AI-driven optimization and human ingenuity yielded a building that surpassed the potential attainable through either a purely computational or strictly traditional design approach.
What is the role of Artificial Intelligence ?
The integration of artificial intelligence design tools into the construction industry opens up possibilities that were once considered highly complex, making them more attainable than ever. These AI-driven design tools empower architects and engineers to conceptualise and refine intricate structural plans with an unprecedented level of precision and efficiency. They enable the exploration of innovative materials, shapes, and sustainable solutions, resulting in structures that not only impress aesthetically but also adhere to environmental responsibilities. Additionally, AI design tools contribute to predictive modelling, foreseeing potential challenges, thereby enhancing safety and reducing costly errors during construction.
Megan Gallagher, a health planner at HDR and a D4O volunteer, expresses her curiosity about the progression of AI as a design tool.
Paul Harrison acknowledges that design outputs inherently carry biases but believes that by training AI on smaller datasets, these biases can be controlled. Initially, HDR found AI invaluable for design optimization. More recently, the firm has embraced AI as a tool for early-stage ideation. Harrison highlights a hospital design project in Kingston, Ontario, where AI served as an ideation tool and humorously notes, “AI is better at coming up with what I like than I am.” He concludes, “AI is quicker for ideation, but it will take some time to perfect the tool for larger projects.”
The Future Impact of the Baruipur Clinic
Upon completion, the Baruipur clinic will provide vital healthcare services, including eye and dental care, X-rays, maternal and paediatric care, and telemedicine. The hub will serve about a half-dozen people as well as multiple villages that include remote islands in the Sundarbans Delta, where diagnostics will be accessible through portable handheld devices, says Jason-Emery Groën, Vice President and Design Director for HDR’s Kingston office. He further highlights HDR’s focus on projects with significant community impact and a high likelihood of realisation.
Discussions are ongoing between D4O and iKure regarding further expansion plans, although the clinic’s construction schedule has been affected by factors like land reviews, pandemic-related labour and material shortages, and extended monsoon seasons, potentially delaying its completion until 2024.
References: bdcnetwork.com, medicalbuyer.co.in, fastcompany.com, hdrinc.com/portfolio/ikure, hdrinc.com


