Concrete admixtures are used to improve the behavior of concrete under a variety of conditions. Concrete admixtures reduce the cost of construction, modify properties of hardened concrete, ensure quality of concrete during mixing/transporting/placing/curing, and overcome certain emergencies during concrete operations. There are two major classifications of admixtures used in concrete – Mineral admixtures and Chemical admixtures.
In this article we will analyze both Mineral admixtures and Chemical admixtures.
What are the advantages of mineral admixtures in concrete?
- Mineral admixtures react chemically with the weaker calcium hydroxide released from the hydration of cement to form stronger calcium silicate hydrates
- This refines the pore structure, reduces the permeability and improves the durability of concrete structures
- Mineral admixtures reduce the heat of hydration of concrete
The mineral admixtures permitted to be used by IS:456:2000 are;
- Fly ash (IS 3812)
- Ground granulated blast furnace slag (IS 12089)
- Silica fume (IS 15388)
- Rice husk ash
- Metakaoline
What are the permissible limits of replacement of fly ash, slag, metakaoline and silica fume admixtures in concrete?
The permissible limits of replacement are-
- Fly ash constituent shall not be less than 15% and not more than 35% by mass of cement (as per Table 5 of IS: 456:2000 and amendment 3 of IS: 1489 – Part I)
- Slag constituent shall be not less than 25% nor more than 70% by mass of cement (as per Table 5 of IS: 456:2000 and amendment 4 of IS: 455)
- Metakaoline and Silica fume are usually used in proportion of 5 to 10% of the cement content of a mix
What are the advantages of metakaoline and silica fume in concrete admixture?
The advantages are-
- Metakaoline and Silica fume may be thought of as an alternate cement replacement material in concrete mixes whose strength requirement exceeds 60 MPa and where there is a restriction in the use of cement content (OPC) beyond 450 Kg/cum
- Average size of metakaoline and silica fume is about 0.1 micron and this is several times smaller than a cement particle. This enables better particle packing or micro filling between cement particles
- Thus the transition zone(thin layer between the hydrated cement paste and the aggregate) is improved due to the physical effect of filling as well as the chemical effect of silica fume converting the weak calcium hydroxide into a stronger calcium silicate hydrate
- This results in enhanced permeability and strength characteristics of concrete
- Metakaoline is cheaper that microsilica and needs less of chemical admixture to get the same workability
- Metakaoline is marketed by 20 Microns limited and Microsilica by Elkem & Corniche in India
What are the distinct classes of chemical admixtures?
The distinct classes are given below;
- Water-reducing (reduce the water demand by 5 to 10%)
- Superplasticisers (reduce the water demand by 12 to 30%)
- Hyperplasticisers (reduce the water demand by 25 to 40%)
- Retarding (slow the setting rate of concrete in hot weather)
- Accelerating (increase the rate of early strength development)
- Air entraining (increased cohesiveness of concrete)
- Viscosity modifying (makes water thicker and reduces segregation)
- Corrosion inhibiting (slow down the corrosion of reinforcement)
- Shrinkage reducing (control drying shrinkage and cracking)
What is the purpose of using High range water reducing admixtures/ Superplasticisers in concrete admixtures?
The purposes are as follows-
- Increases the workability/pumpability without increasing the water content and water/cement ratio
- Improves the cohesiveness and reduces segregation and bleeding
- Improves set retardation as generally Type G (as per ASTM) Superplasticisers are used
The workability of concrete improves due to the use of Superplasticisers in admixtures for concrete
- The long molecules in the Superplasticiser wrap themselves around the cement particles and give them a highly negative charge and this repels the cement particles
- This results in deflocculation and dispersion of the cement particles
- The resulting deflocculation releases the entrapped water between the cement particles, thus improving the workability
How the Superplasticiser dosage is calculated in concrete admixtures?
The process is-
- The Superplasticiser dosage is calculated as a percentage (%) by weight or volume of cement.
- Arriving at the optimal dosage of Superplasticiser is very important
- Dosage beyond the optimal dosage may be detrimental and can cause segregation, bleeding or excessive retardation, which can be harmful to concrete
What are the precautions required to be taken when using Superplasticers in concrete admixtures?
The precautions taken are as follows.
- All Superplasticers should be tested adequately for their desired performance in full scale before being used in any large scale construction work
- It is important to do trial mixes using the Superplasticiser with the same concrete materials proposed to be used at site including the brand, grade and type of cement
- Never use a Superplasticser from an unmarked container
- Superplasticser should be free from chlorides and sulphates
- If Superplasticser are to be used after a lapse of time, it is essential to stir the contents in the container before using it. The shelf life of the Superplasticiser could be varying between 6 months to 1 year as per the manufacturer, but it should be stored in the original container and protected from sunlight
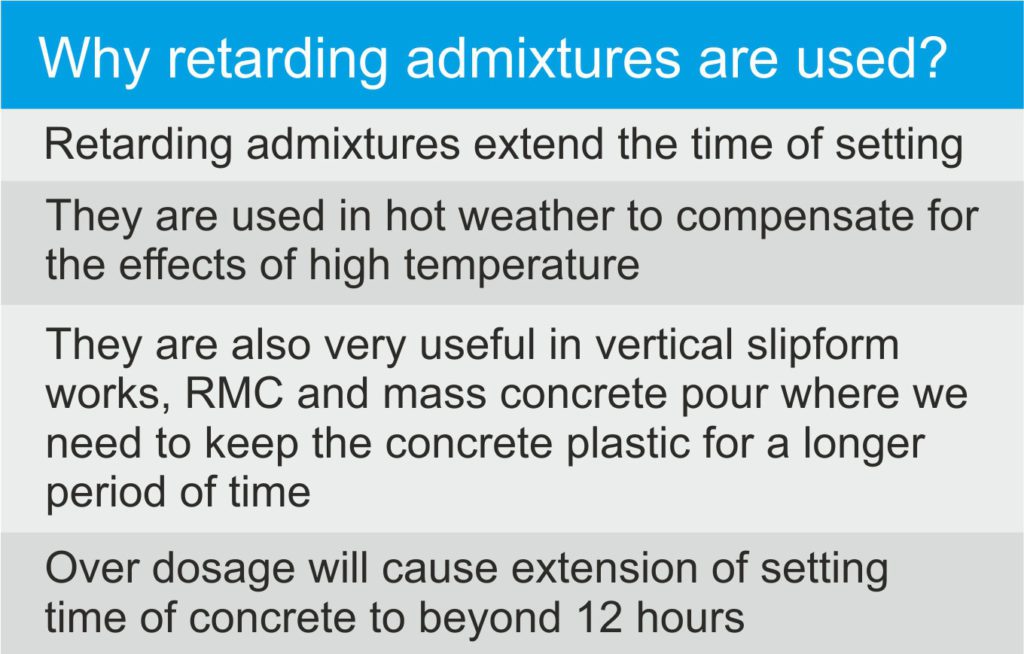
What is the most commonly used accelerating admixture and what precautions are necessary in its use?
The precautions needed to be taken care of are-
- Calcium chloride. It should not be used in amounts in excess of 2%, preferably 1% of the mass of cementitious materials and only in solution form
- To minimize corrosion, calcium chloride should not be used in steel reinforced concrete or where there is an aluminium conduit in the concrete
- Non-chloride accelerating admixtures are available and they should be used in steel reinforced concrete
Why air entraining admixtures are used?
The reasons are-
- Air entraining admixtures improve the cohesiveness of concrete and mortar
- They are normally dosed at 50 to 150 ml per bag of cement
- They are used in pumpable concrete/mortar making and concreting of slender/tall sections. They are also used in horizontal slipform paving of canals and road kerbs.
- Over dosage will cause loss of strength (5% for every 1% of additional air)
Why viscosity modifying admixtures are used?
The specified reasons are-
- Viscosity modifying admixtures improve the cohesiveness of concrete
- They are normally dosed at 50 to 100 ml per bag of cement
- They are used in self compacting concrete using cement content of less than 400 Kg per cu.m. of concrete. Cement content includes mineral admixtures
Summary
The most common mineral admixtures used in concrete are fly ash, slag, metakaoline and silica fume. The addition of mineral admixtures reduces the permeability and improves the durability of concrete structures. In addition, the heat of hydration of concrete is considerably reduced due to the addition of mineral admixtures The use of High range water reducing admixtures/Superplasticisers increases the workability/pumpability of concrete mixes without increasing the water content and water/cement ratio. The addition of Superplasticiser also improves the cohesiveness and reduces segregation and bleeding.
Author

About Author – Author’s areas of research include Concrete Technology, Non- Destructive testing of RC structures and Repair and Rehabilitation of RC structures. He is involved in more than 150 consultancy projects for various Government, Public Sector and Private agencies, including Defense and Nuclear departments.





