In construction where heights pose a risk, ensuring comprehensive fall protection is paramount. As industries advance and workplaces diversify, it becomes imperative to comprehend and implement effective measures for fall protection. This article delves into the crucial aspects of fall protection, examining its significance, equipment and accessories used that enhance a safer working environment.
What is a Fall Protection System?
A Fall Protection System encompasses safety measures and equipment meticulously designed to prevent or minimize falls during elevated work activities. The importance of a fall protection system lies in safeguarding the well-being of workers and minimizing the risks associated with working at heights. Falls from elevated surfaces are a leading cause of workplace injuries and fatalities. Implementing an effective fall protection system not only helps in compliance with safety regulations but also promotes a culture of workplace safety.

Types of Fall Protection Systems
- Fall Arrest: Safeguards workers at heights.
- Fall Restraint: Applied when workers need to operate on the edge of a hazard.
- Fall Prevention: Eliminates fall risks by averting the need for work at heights.
Types of Fall Protection Measures
- Collective Protection: Acts as a control measure safeguarding everyone.
- Personal Protection: Focuses on individual safety, requiring personal responsibility.
- Access and Rescue Protection; Provide safe entry and exit from elevated work areas.
Different types of equipments used for fall protection
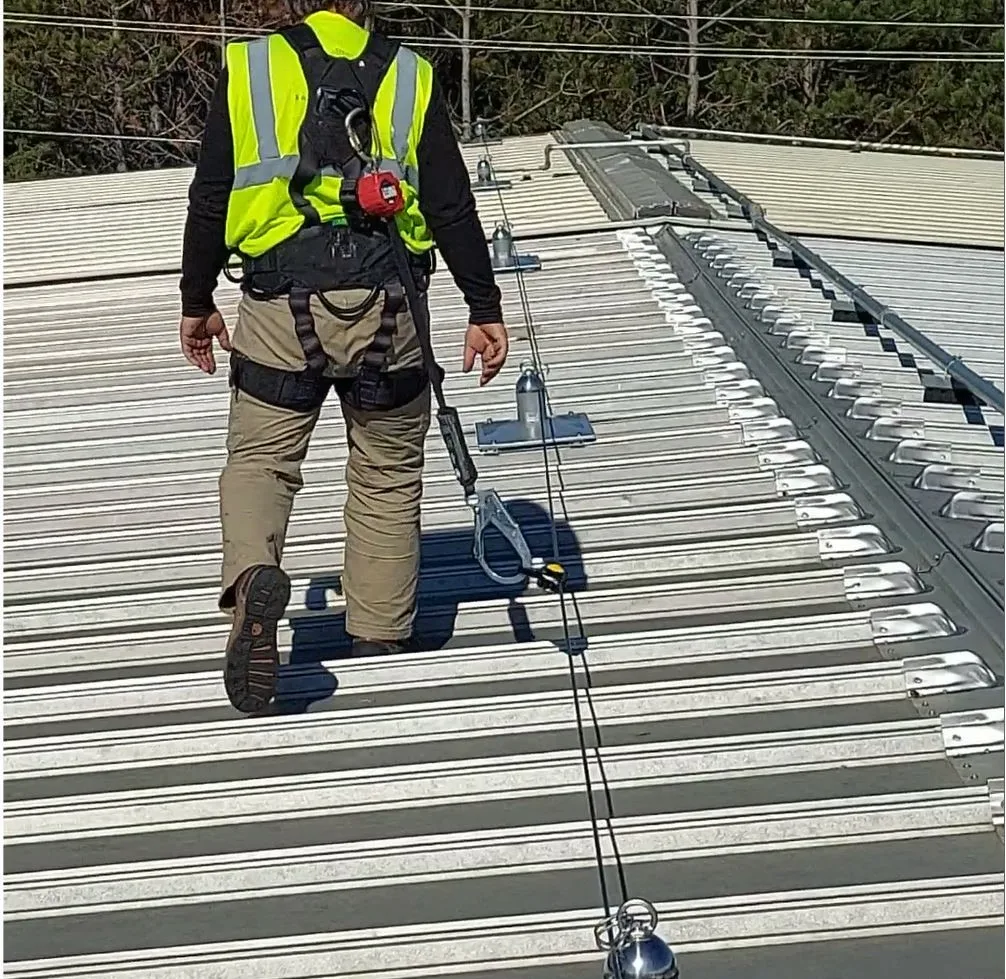
Personal Fall Protection Equipments :
1. Harnesses: Full Body Harnesses are fundamental components of personal fall protection, enveloping the wearer in a secure webbing that distributes forces evenly. Chest Harnesses, focusing on the upper body, may be employed in situations requiring specialized support. Suspension Trauma Straps, integral to harnesses, mitigate the risk of suspension trauma by allowing the user to stand in their harness after a fall, reducing pressure on the legs.
2. Lanyards: Shock Absorbing Lanyards play a crucial role in reducing the impact forces generated during a fall, protecting the worker from injury. Positioning Lanyards provide flexibility for positioning while working at height, enhancing comfort and efficiency. Retractable Lanyards automatically adjust their length, minimizing slack in the system and providing freedom of movement when needed.
3. Anchorage Points: Roof Anchors, secured to roofs, serve as stable attachment points for fall protection systems. Beam Straps are designed for attachment to beams or other structural elements, ensuring a reliable anchor. D-rings and Anchor Plates are key components, providing secure connection points for lanyards or lifelines.
4. Connectors: Carabiners are versatile connectors used to link various elements of the fall protection system. Snap Hooks offer quick and secure connections, facilitating efficient attachment and detachment. D-ring Extenders extend the reach of attachment points, accommodating specific work requirements.
5. Horizontal Lifeline Systems: Tailored for horizontal surfaces, these systems consist of cables or tracks along which users can attach themselves, effectively preventing falls. Horizontal lifeline systems offer flexibility of movement while maintaining a secure connection, making them vital for safeguarding workers on flat or gently sloping workspaces.
6. Vertical Lifelines: Similar to their horizontal counterparts, vertical lifeline systems are designed for applications where secure attachment is needed in vertical orientations. These systems offer a dependable means for preventing falls in scenarios where workers operate on surfaces with significant vertical inclines.
7. Body Belts & Work Seats: Forming components of a fall protection system, body belts, and work seats provide support and restraint for workers engaged in elevated tasks. These elements are designed to distribute forces throughout the body, enhancing comfort and safety during prolonged periods of work at heights.
8. Self-Retracting Lifelines: Offering automatic retraction of lifelines, these devices minimize slack and reduce the risk of tripping or entanglement. Self-retracting lifelines provide an additional layer of safety by ensuring that excess slack is minimized, contributing to a more secure working environment.

Collective Fall Protection Equipments:
1. Guardrails: Portable Guardrails, easily deployable, act as temporary barriers on elevated surfaces, preventing accidental falls. Permanent Guardrails are fixed structures strategically installed for long-term fall prevention, providing a continuous barrier along exposed edges.
2. Safety Nets: Vertical Safety Nets are positioned vertically to catch falling workers or debris, acting as a last line of defense. Horizontal Safety Nets, installed horizontally, offer protection from falls in elevated work areas, minimizing the risk of injury.
3. Safety Fences: Warning Lines establish visible boundaries, warning workers of hazardous areas and restricting access. Perimeter Fencing creates a physical barrier around construction zones, enhancing overall site safety.

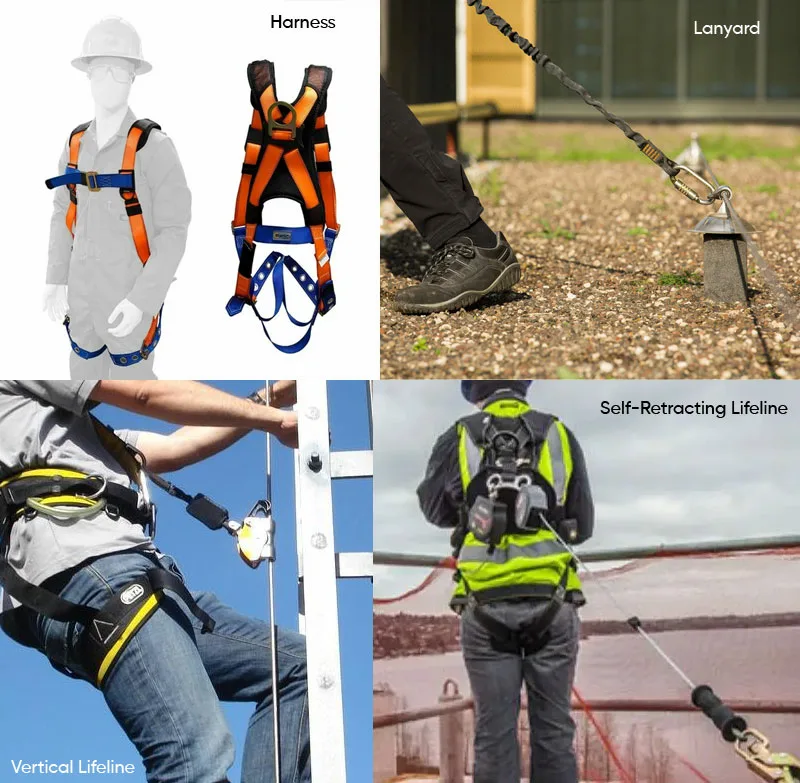
Access and Rescue Equipments:
1. Ladder Safety Systems: Vertical Lifelines attached to ladders serve as a vital component in fall arrest systems, ensuring safety during ladder use. Ladder Brackets securely attach ladders, preventing slippage and enhancing stability.
2. Rescue Kits: Controlled Descent Devices are critical for emergency situations, allowing for a controlled descent in the event of a fall. Rescue Poles assist in reaching and retrieving a fallen worker, facilitating prompt and effective rescue operations.
3. Climbing Equipment: Climbing Ropes are essential tools for vertical ascent and descent, providing stability and support. Climbing Harnesses securely distribute weight, enhancing comfort and safety during climbing activities.
4. Load Arrestors: Load arrestors are devices specifically engineered to halt a falling load, preventing injury or damage in the event of a fall. These devices are crucial for maintaining safety in situations where heavy objects are involved, offering a reliable mechanism to mitigate the consequences of a potential fall.
5. Connected Safety RFID Systems: Incorporating technology such as Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) enhance safety monitoring and compliance in fall protection. By utilizing advanced tracking and identification methods, connected safety RFID systems contribute to improved oversight and management of fall protection measures, promoting a higher level of workplace safety.

Types of Fall protection accessories
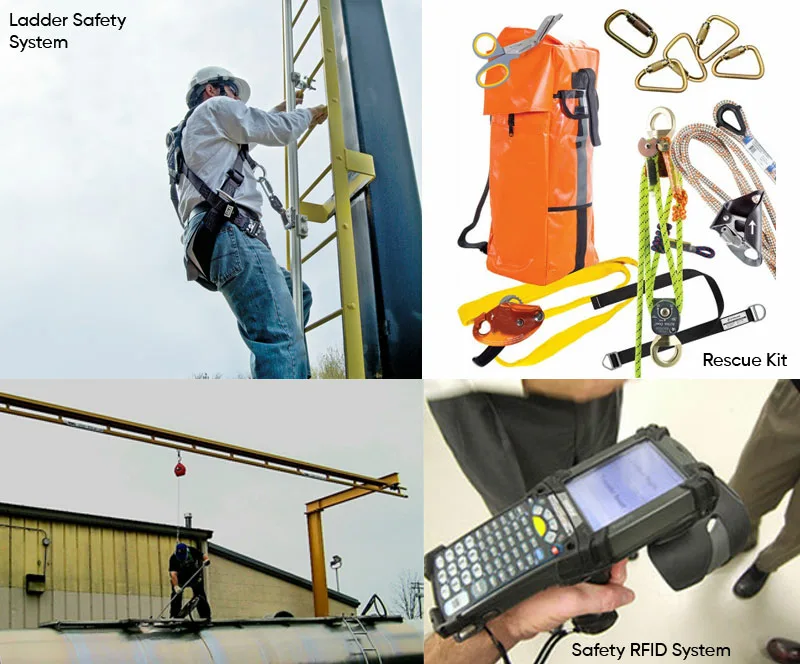
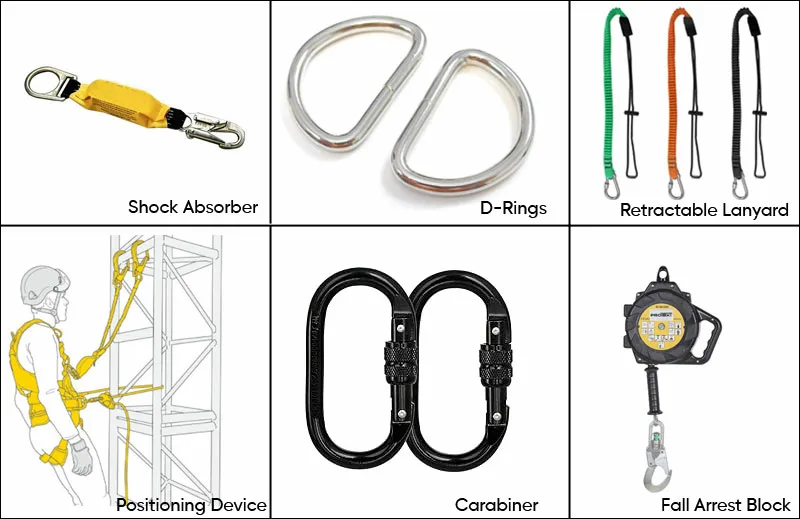
Fall protection accessories complement the primary equipment in a fall protection system, enhancing safety and functionality. Some common fall protection accessories include:
1. Shock Absorbers: Attachments that reduce the impact force on the body during a fall.
2. Positioning Devices: Allows a worker to be supported in place while working at heights.
3. D-Rings and Connectors: Attachment points on harnesses and other equipment for connecting lanyards or lifelines.
4. Carabiners: Used to connect various components of the fall protection system.
5. Retractable Lanyard Fall Indicators: Provide a visual indication if the lanyard has been subjected to a fall.
6. Fall Arrest Blocks: Compact devices that arrest falls, often used in confined spaces.
7. Anchor Slings: Straps or ropes used to create secure anchor points.
8. Cable Grabs: Devices that automatically grip the lifeline in the event of a fall.
9. Tool Tethers: Secures tools to prevent them from falling.
10. Harness Accessories: Pouches, tool belts, or additional padding to enhance comfort and functionality.
Consideration for selection of fall protection equipments and accessories
When using fall protection equipment and tools, several key considerations are essential to ensure their effectiveness and the safety of workers:
1. Proper Training: Ensure that workers are adequately trained in the correct use of fall protection equipment. Training should cover proper fitting, adjustment, attachment, and inspection procedures.
2. Equipment Inspection: Regularly inspect all fall protection equipment for wear, damage, or other defects. Damaged equipment should be taken out of service immediately and replaced.
3. Appropriate Equipment Selection: Select fall protection equipment suitable for the specific task and working conditions. This includes choosing the right type of harness, lanyard, anchorage point, and any additional tools required.
4. Anchorage Points: Verify that anchorage points are secure and capable of supporting the anticipated load. Follow manufacturer guidelines and use only designated and approved anchorages.
5. Clear Work Area: Keep the work area clear of potential hazards and obstacles that could lead to trips or falls. Adequate housekeeping is essential for maintaining a safe environment.
6. Inspect Tools and Tethering: When using tools at heights, inspect them regularly, and ensure that they are securely tethered to prevent accidental drops. Tool tethers and lanyards should be appropriately rated for the weight of the tools.
7. Fall Distance Consideration: Be aware of the fall distance and select equipment that allows for a safe arrest within that distance. Consider the use of shock-absorbing lanyards to reduce the impact on the body in the event of a fall.
8. Rescue Plan: Develop and communicate a clear rescue plan in case a fall occurs. Ensure that all workers are familiar with the procedures and that necessary rescue equipment is readily available.
9. Comfort and Fit: Ensure that fall protection equipment is comfortable and correctly fitted to each worker. Ill-fitting equipment can lead to discomfort, reduced effectiveness, or even failure during a fall.
10. Communication: Establish clear communication protocols among workers involved in tasks requiring fall protection. Effective communication is crucial for coordinating activities and responding to emergencies.
Always refer to the OSHA standards (29 CFR 1926 Subpart M for construction, and 29 CFR 1910.28 for general industry) for comprehensive information and compliance details. It’s important to stay updated with the latest OSHA regulations and consult with safety professionals to ensure a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Prioritizing fall protection is paramount in ensuring workplace safety. The array of fall protection equipment and accessories discussed in the article highlights the diverse options available for safeguarding workers at heights. From harnesses and lanyards to guardrails and anchors, employers must invest in comprehensive solutions tailored to their specific needs. Regular training on proper usage and maintenance further enhances the effectiveness of these measures, fostering a secure work environment and reducing the risk of accidents. Ultimately, a proactive approach to fall protection not only complies with regulations but, more importantly, safeguards the well-being of those working at elevated levels.





