Steel is the material of choice for design because it is inherently ductile and flexible. It flexes under extreme loads rather than crushing and crumbling. Structural steels low cost, strength, durability, design flexibility, adaptability and recyclability continue to make it the material of choice in building construction. Fast construction lowers overhead expenses for construction management services. Steel is extensively used in the construction of industrial buildings of large spans with or without cranes (medium and heavy buildings), where the concrete construction is not feasible.
In structural engineering, a pre-engineered building (PEB) is designed by a manufacturer to be fabricated using a predetermined inventory of raw materials and manufacturing methods that can efficiently satisfy a wide range of structural and aesthetic design requirements. Pre-engineered steel buildings can be fitted with different structural accessories including mezzanine floors, canopies, fascia’s, interior partitions etc. and the building is made water proof by use of special mastic beads, filler strips and trims.
In pre-engineered building concept the complete designing is done at the factory and the building components are brought to the site in knock down condition. An efficiently designed pre-engineered building can be lighter than the conventional steel buildings by up-to 30%. Lighter weight equates to less steel and a potential price savings in structural framework.
A Hangar is a closed structure to hold aircraft or spacecraft in protective storage. Hangars are used for protection from weather, protection from direct sunlight, maintenance, repair, manufacture, assembly and storage of aircraft on airfields, aircraft and ships. Hangars need special structures to be built. The width of the doors is too large and spans from 30 meters to 120 meters, thus enables the aircraft entrance. The bigger the aircraft are to be introduced, the more complex structure is needed. Hence Pre-Engineered buildings are specially designed and engineered to fit together to satisfy the unique requirements of specific end-uses.
1. INTRODUCTION
Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs) are the latest trend in India. A PEB is a metal building that consists of light gauge metal standing seam roof panels on steel purlins spanning between rigid frames with light gauge metal wall cladding. They drastically reduce construction time. Maintenance is also extremely low. PEBs optimally utilize resources, and leverage technology to the maximum. Pre engineered buildings have gained a global reputation for durability, water and earthquake resistance. PEBs are tremendously versatile – they are easy to set-up, expand, modify, and transport to different locations. They are environmentally friendly and can be aesthetically designed with unique features. An estimated 20-30% can be saved on cost, as compared to conventional building methods.
PEBs can be delivered to a site in just 5 to 8 weeks -conventional steel structures take as much as 20 to 25 weeks to complete. The unique techniques employed during fabrication help PEBs be up-to 30% lighter than regular steel products. No welding or fabrication is required at the construction site, resulting in greater speed and efficiency.
2. CLASSIFICATION OF BUILDINGS
A healthy trend in the form of growth in demand for construction works in residential, Commercial, Institutional, Industrial and Infrastructure sectors are being seen over the past decade. Modern Structures are much more complex and sophisticated as compared to earlier period. One of the major changes which are being felt by all is that the present structures are taller and thinner. Modern day requirement of structures is that these should be lighter yet not compromising on functionality. Civil engineering construction has seen a continual economic competition between steel, concrete and other construction materials.
2.1 Reinforced Cement Concrete Buildings
Reinforced concrete is concrete in which reinforcing bars have been integrated to improve one or more properties of the concrete. For many years, it has been utilized as an economical construction material in one form or another. A large part of its worldwide appeal is that the basic constituent materials cement, sand, aggregate, water, and reinforcing bars are widely available and that it is possible to construct a structure using local sources of labor and materials.
2.2 Steel Buildings
A steel building is a metal structure fabricated with steel for the internal support and for exterior cladding, as opposed to steel framed buildings which generally use other materials for floors, walls, and external envelope. Steel buildings are used for a variety of purposes including storage, workspaces and living accommodation.
2.3 Timber Buildings
Timber Buildings are more feasible in areas where wood materials are easily accessible, wood construction is often considered to be the cheapest and best approach for small housing structures. Wooden or timber buildings are constructed in western countries where temperatures are too low. In wooden buildings the members such as beams, columns and roofs are made of wood. The wooden buildings may be in thatched, gypsum and plywood sheeting etc.
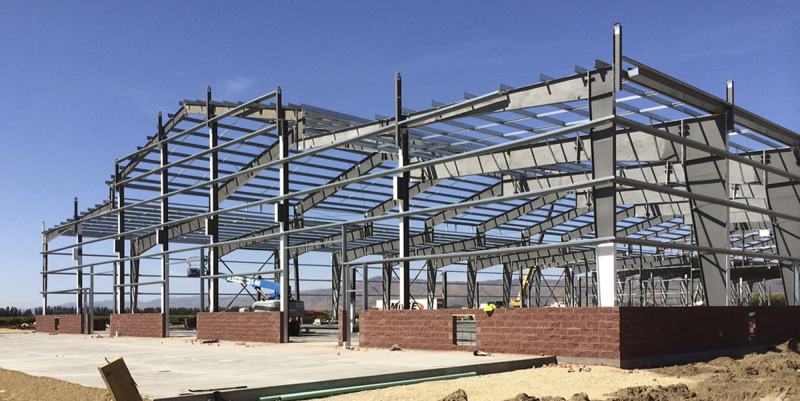

3. STEEL BUILDINGS
Today’s structural steel framing is bringing grace, art and function together in almost limitless ways and is offering new solutions and opportunities to create challenging structures, which were once thought impossible. Steel structures have reserve strength. Simple stick design in the steel framing allows construction to proceed rapidly from the start of erection.
3.1 Conventional Steel Buildings
Conventional Steel buildings are consultant and conservative. The Structural members are hot rolled and are used in conventional buildings. The materials are produced or manufactured in the plant and are shifted to the site. The raw materials are processed in the site for the desired form and erected. The modifications can be done during erection by cut and weld process. Truss systems are used in conventional system.
3.2 Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings
Pre-Engineered Steel Buildings are manufactured or Produced in the plant itself. The manufacturing of structural members is done on customer requirements. The detailed structural members are designed for their respective location and are numbered, which cannot be altered, because members are manufactured with respect to design features. These components are made in modular or completely knocked condition for transportation. These materials are transported to the customer site and are erected. Welding and cutting process are not performed at the customer site. No manufacturing process takes place at the customer site.
The most common and economical type of low rise buildings is a building with ground floor and two intermediate floor plus roof. The roof of low rise buildings may be flat or sloped. Intermediate floors of low rise buildings are made of mezzanine systems. Single storied houses for living take minimum time for construction and can be built in any type of geographical location like extreme cold hilly areas, high rain prone areas, plain land obviously and extreme hot climatic zones as well.
4. ADVANTAGES OF PEBs
- Reduction in Construction Time: Buildings are typically delivered in just a few weeks after approval of drawings. Foundation and anchor bolts are cast parallel with finished, ready for the site bolting. In India the use of pre engineered buildings will reduce total construction time of the project by at least50%. This also allows faster occupancy and earlier realization of revenue.
- Lower Cost: Due to the systems approach, there is a significant saving in design, manufacturing and on site erection cost. The secondary members and cladding nest together reducing transportation cost.
- Flexibility of Expansion: Buildings can be easily expanded in length by adding additional bays. Also expansion in width and height is possible by pre designing for future expansion.
- Larger Spans: Buildings can be supplied to around 80M clear spans.
- Quality Control: As buildings are manufactured completely in the factory under controlled conditions the quality is assured.
- Low Maintenance: Buildings are supplied with high quality paint systems for cladding and steel to suit ambient conditions at the site, which results in long durability and low maintenance costs.
- Energy Efficient Roofing and Wall Systems: Buildings can be supplied with polyurethane insulated panels or fiberglass blankets insulation to achieve required U values.
- Architectural Versatility: Building can be supplied with various types of fascia’s, canopies, and curved eaves and are designed to receive precast concrete wall panels, curtain walls, block walls and other wall systems.
- Single Source Availability: As the complete building package is supplied by a single vendor, compatibility of all the building components and accessories is assured. This is one of the major benefits of the pre-engineered building systems.
5. APPLICATION OF PEB
Almost every conceivable building use has been achieved with PEB; the most common applications are industrial, institutional and commercial buildings.
In India, Pre-engineered building systems find application primarily in the construction of Warehouses, & Industrial sheds & Buildings. The recent focus has also shifted to cover rural as well as urban, individual and mass housing projects, farmhouses, slum re-organization projects and rehabilitation projects, amenity structures like health centers, kiosks, primary schools, panchayat etc. The pharmaceutical industries and exhibition centers, and functional requirements like offices, seminar halls, call centers, supermarkets, showrooms etc. have also attracted PEB. Earthquake-resistant buildings are the recent applications of PEB with wide and immediate acceptance.
5.1 Applications of Pre Engineered steel buildings include:-
- Houses & Living Shelters.
- Factories.
- Warehouses.
- Sports Halls (Indoor and Outdoor).
- Aircraft Hangers.
- Supermarkets.
- Workshops.
- Office Buildings.
- Labour Camps.
- Petrol Pumps/Service Buildings.
- Schools.
- Community centers.
- Railway Stations
- Equipment housing/shelters.
There is a great possibility of improving the aesthetic quality with a choice of roofing elements, exterior finishes, weather-sheds, color system and variations in planning as well as massing.
6. PEB PROSPECT S IN THE WORLD
Technological improvement over the years has contributed immensely to the enhancement of quality of life through various new products and services. One such revolution was the pre engineered buildings. Through its origin can be traced back to 1960s its potential has been felt only during the recent years. This was mainly due to the development in technology, which helped in computerizing the design. PEB concept has been very successful and well established in North America, Australia and is presently expanding in UK and European countries. PEB construction is 30 to 40% faster than masonry construction. PEB buildings provide good insulation effect and would be highly suitable for a tropical country like India. PEB is ideal for construction in remote & hilly areas. A recent survey by the Metal Building Associations (MBA) shows that about 60% of the nonresidential low rises building in USA are pre-engineered buildings.
7. PEB PROSPECTS IN INDIA
Although PEB systems are extensively used in industrial and many other nonresidential constructions worldwide, it is relatively a new concept in India. These concepts were introduced to the Indian markets lately in the late 1990s with the opening up of the economy and a number of multinationals setting up their projects. India has an installed steel capacity of 35 to 40 million tones & apparent steel consumption is around 27 to 30 million tones. The current Pre-Engineered steel building manufacturing capacity is 0.35 million tons per annum. The industry is growing at a compound rate of 25 to 30 %.
8. FUTURE OF PEB
The steel structures (SS) market in India is in excess of 4.5 Mn.MT, growing at a rapid pace of more than 10% p.a. over the past few years. This market has experienced a higher growth compared to both Indian steel industry as well as Indian construction GDP. Overall construction sector accounts for majority (greater than 80%) of the steel structures market (volume terms) in India.
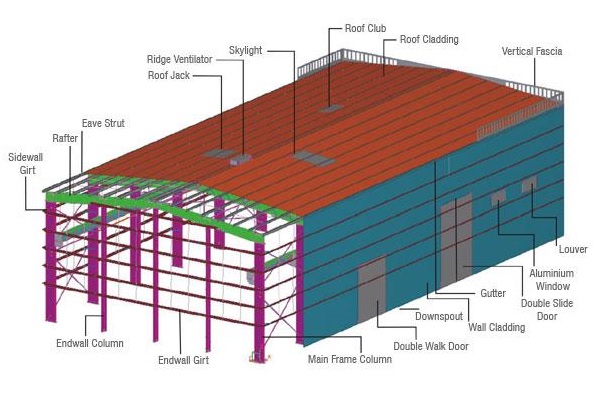
9. COMPONENTS OF PEB
A typical assembly of a simple metal building system is shown below to illustrate the Synergy between the various building components as described below:
- Primary components.
- Secondary components.
- Sheeting (or) cladding.
- Accessories.
9.1 PRIMARY COMPONENTS
A. Main framing
Main framing basically includes the rigid steel frames of the building. The PEB rigid frame comprises of tapered columns and tapered rafters (the fabricated tapered sections are referred to as built-up members). The tapered sections are fabricated using the state of art technology wherein the flanges are welded to the web. Splice plates are welded to the ends of the tapered sections. The frame is erected by bolting the splice plates of connecting sections together. All rigid frames shall be welded built-up “I” sections or hot-rolled sections. The columns and the rafters may be either uniform depth or tapered. Flanges shall be connected to webs by means of a continuous fillet weld on one side. All end wall roof beams and end wall columns shall be cold-formed “C” sections, mill-rolled sections, or built-up “I” sections depending on design requirements. Plates, Stiffeners, etc. All base plates splice plates, cap plates, and stiffeners shall be factory welded into place on the structural members. Built-up I section to build primary structural framing members (Columns and Rafters).
B. Columns
The main purpose of the columns is to transfer the vertical loads to the foundations. However apart of the horizontal actions (wind action) is also transferred through the columns. Basically in pre-engineered buildings columns are made up of I sections which are most economical than others. The width and breadth will go on increasing from bottom to top of the column. I section consists of flanges and web which are made from plates by welding.
C. Rafter
A rafter is one of a series of sloped structural members (beams) that extend from the ridge or up-to the wall-plate, down slope perimeter or eave, and that are designed to support the roof deck and its associated loads.
9.2 SECONDARY COMPONENTS
Purlins, Grits and Eave struts are secondary structural members used as support to walls and roof panels. Purlins are used on the roof, Grits are used on the walls and Eave struts are used at the intersection of the sidewall and the roof. They are supplied with minimum yield strength of 34.5KN/m. Secondary member’s act as struts that help in resisting part of the longitudinal loads that are applied on the building such as wind and earthquake loads and provide lateral bracing to the compression flanges of the main frame members for increasing frame capacity. Purlins, Grit-sand Eave struts are available in high grade steel conforming to ASTM 607 Grade 50 or equivalent, available in 1.5 mm, 1.75 mm. 2.0 mm, 2.25 mm, 2.5 mm and 3.0 mm thickness. They come with a pre-galvanized finish, or factory painted with a minimum of 35 microns (DFT) of corrosion protection primer. Purlins and girts shall be cold-formed “Z” sections with stiffened flanges. Flange stiffeners shall be sized to comply with the requirements of the latest edition of AISI.
9.3 SHEETING OR CLADDING
The sheets used in the construction of pre-engineered buildings are composed of the following: Base metal of either Galvalume coated steel conforming to ASTM A 792 M grade 345B or aluminum conforming to ASTM B 209M. Galvalume coating is 55% Aluminum and about45% Zinc by weight. An exterior surface coating on painted sheets of 25 microns of epoxy-primer with a highly durable polyester finish. An interior surface coating on painted sheets of 12 microns of epoxy primer and modified polyester or foam. The sheeting material is cold-rolled steel, high tensile 550 MPA yield stress, with hot dip metallic coating of Galvalume sheet.
9.4 ACCESSORIES
- Window
- Ridge Ventilator
- Sliding Door
- Roll up Shutter
- Turbo Ventilator
- Roof Skylight
- Adjustable Louvre
- Insulation
- Ladder with Safety Cage

10. CONCLUSION
Steel is such a versatile material that every object we see in our daily life has used steel direction indirectly. There is no viable substitute to steel in construction activities.
Steel remains and will continue to remain logical and wide choice for construction purpose environmentally also as much of the steel used is recycled. Steel building offers more design and architectural flexibility for unique or conventional styling. Its strength and large clear spans mean the design is not constrained by the need for intermediate support walls. As your requirements changes over the years, you can reuse, relocate & modify the structure.
Pre-engineered Metal building concept forms a unique position in the construction industry in view of their being ideally suited to the needs of modern Engineering Industry. It would be the only solution for large industrial enclosures having thermal and acoustical features. The major advantage of metal building is the high speed of design and construction for buildings of various categories.
Authored by;






