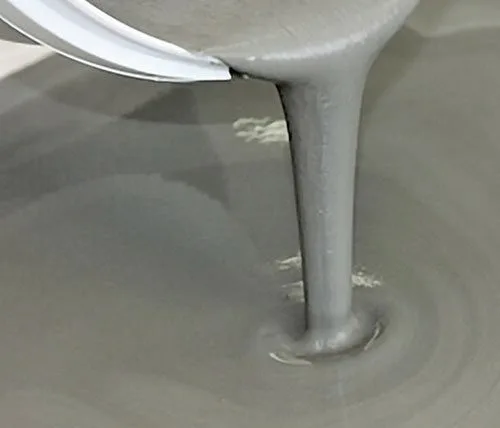
Cementitious grout is a cement-based material used to fill voids and cracks in buildings and structures. It is a fluid mixture made of cement, sand, and water, enhanced with additives to improve flowability, strength, and shrinkage resistance. Its stability and adaptability to various site conditions make it a reliable and versatile choice for a wide range of applications.
Uses of Cementitious Grouts:
- Filling Voids
- Anchoring
- Repairing Concrete
- Precast Connections
- Structural Strengthening
- Machinery Installation
- Waterproofing
- Foundation Grouting
- Soil Stabilization
- Underpinning
Advantages of Cementitious Grouts
- Provides excellent compressive and tensile strength for structural support.
- Minimize shrinkage, ensuring a stable and secure bond.
- imple mixing and placement make it user-friendly.
- Creates a strong bond with surrounding materials like concrete and masonry.
- High fluidity allows it to penetrate small voids.
- Performs well under varying temperature conditions.
- Resists damage from chemicals in industrial and environmental settings.
- Properties can be adjusted with additives to meet specific project needs.
- Fast Setting: Sets quickly, reducing downtime during construction or repairs.
- Effective in waterproofing applications, preventing moisture infiltration.
- Distributes weight evenly across the bonded area, preventing stress points.
- Resists damage from freeze-thaw cycles in cold climates.
Types of Cementitious Grouts
Standard Cementitious Grout
Standard cementitious grout is a simple mixture of cement, sand, and water, commonly used for general-purpose applications. It is ideal for filling small voids and cracks in concrete or masonry structures, especially in low-stress environments where high strength is not a critical factor. The key advantages of standard grout are its cost-effectiveness and ease of application. It provides a solid bond and ensures good adhesion to surrounding materials, making it suitable for routine maintenance and minor repairs.

High-Strength Cementitious Grout
High-strength cementitious grout is formulated with additional additives to significantly increase its compressive and tensile strength. This type of grout is ideal for use in applications that require heavy load-bearing, such as structural repairs, anchoring steel reinforcements, or filling larger voids in high-stress areas. The main benefits of high-strength grout are its durability and ability to perform under intense mechanical loads, making it the preferred choice for infrastructure projects such as bridges, foundations, and load-bearing columns.
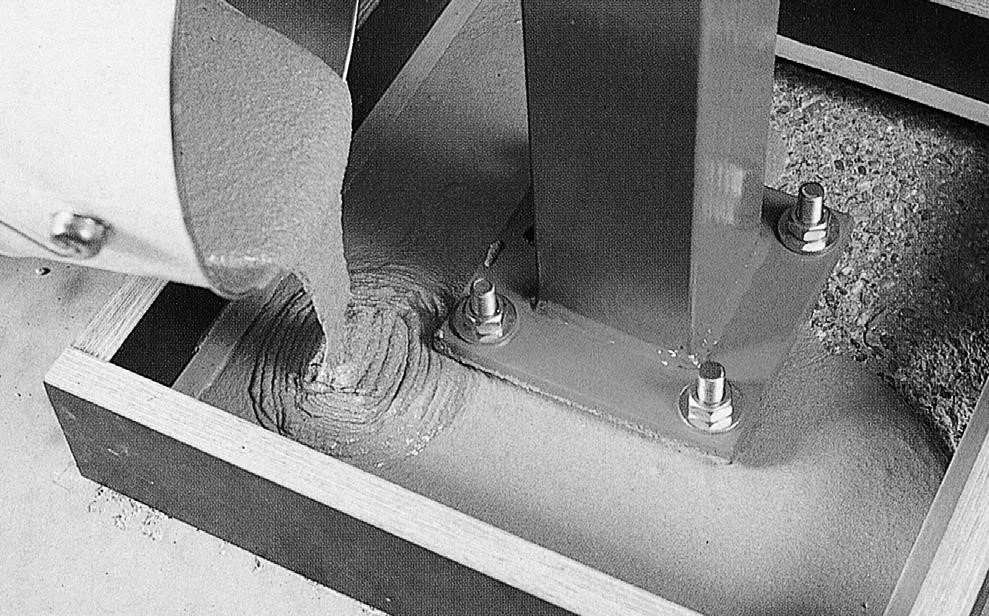
Non-Shrink Cementitious Grout
Non-shrink cementitious grout contains special additives that prevent shrinkage during the curing process, ensuring that the grout remains stable and fills gaps completely. This grout is widely used for anchoring bolts, securing machinery, and filling voids in critical applications. The primary advantage of non-shrink grout is its ability to maintain its volume over time, preventing gaps or voids that could compromise structural integrity.
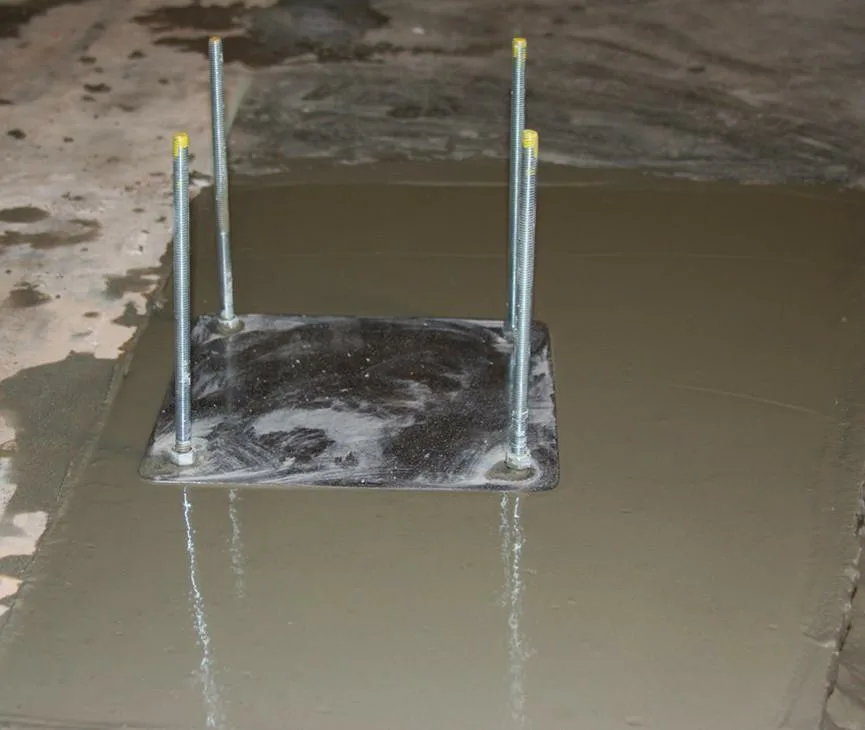

Self-Leveling Cementitious Grout
Self-leveling cementitious grout has high fluidity, allowing it to spread and level itself without the need for manual finishing. It is perfect for applications where a smooth, uniform surface is required, such as in industrial floors, foundations, and tiling projects. The main benefit of self-leveling grout is its ease of application and its ability to flow into tight spaces and complex geometries without requiring extensive labor. This grout is also ideal for situations where a smooth, even surface is a priority, reducing the need for additional finishing work.

Polymer-Modified Cementitious Grout
Polymer-modified cementitious grout is enhanced with polymers that improve its adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to cracking. This grout is commonly used in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or temperature extremes, where traditional cement-based grouts may fail. The polymer additives provide superior bonding strength, flexibility, and water resistance. This makes polymer-modified grout ideal for high-traffic areas, wet environments such as bathrooms or kitchens, and for applications where durability is paramount.
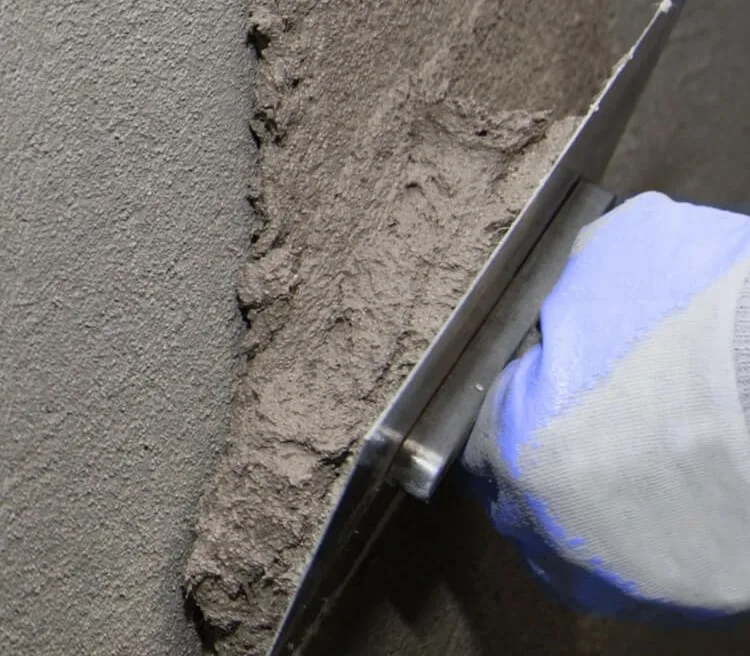

Pumpable Cementitious Grout
Pumpable cementitious grout is designed for projects where the grout needs to be injected into deep or hard-to-reach spaces. This grout is ideal for large-scale infrastructure projects, such as tunnel construction, foundation grouting, or large void filling. The key advantage of pumpable grout is its ability to be pumped over long distances, making it suitable for expansive projects where manual application would be impractical. It also offers excellent flow characteristics, allowing it to fill voids uniformly and efficiently.
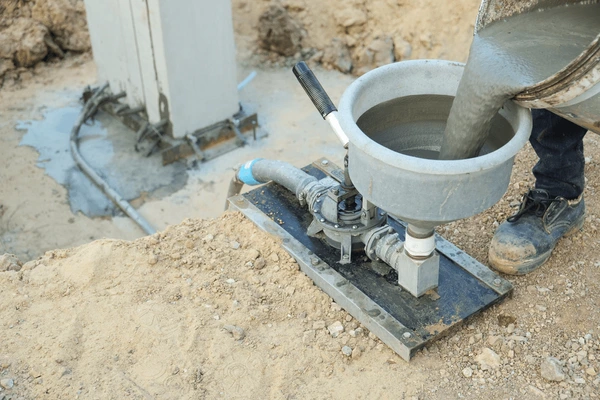

Expansive Cementitious Grout
Expansive cementitious grout contains agents that cause the grout to expand as it cures, helping it fill any voids and ensuring a tight bond with the surrounding materials. This type of grout is perfect for structural repairs where maximum adhesion and volume stability are needed. The expansion helps ensure that the grout fills all gaps without leaving any voids, making it ideal for repairing cracks in concrete or masonry. Expansive grout is also used in foundation repairs and other applications where a secure, tight bond is critical for long-term stability.
Low Heat Cementitious Grout
Low heat cementitious grout is formulated to minimize the heat generated during the curing process. This grout is ideal for large mass pours or applications where high temperatures could lead to cracking or damage. Its main advantage is its ability to maintain the integrity of both the grout and surrounding materials, even in high-heat environments. Low heat grout is commonly used in the construction of large structures such as dams or large foundations, where managing heat during the curing process is important for preventing thermal damage.
Rapid-Setting Cementitious Grout
Rapid-setting cementitious grout is designed to cure quickly, allowing for a fast turnaround time in applications that require minimal downtime. This type of grout is particularly useful for emergency repairs or projects that need to be completed quickly, such as highway repairs or industrial maintenance. The main benefit of rapid-setting grout is its quick curing time, enabling immediate use of the grouted area. It is ideal for situations where quick repairs are essential, and where time constraints require minimal disruption to the site’s operations.
Different methods for applying Cementitious Grouts:
- Manual Application: Applied by hand or trowel for small repairs and voids in accessible areas.
- Pouring Application: Grout is poured into larger voids, cracks, or cavities, typically for filling gaps in foundations or large concrete structures.
- Injection Method: Grout is injected under pressure into tight, hard-to-reach areas like cracks or voids, commonly used in structural repairs.
- Pumpable Application: Uses specialized pumps to transport grout over long distances, ideal for large-scale projects like tunnel lining or deep foundation work.
- Self-Leveling Application: Grout spreads evenly on surfaces, ideal for flooring applications that require a smooth, flat finish.
- Spray Application: Grout is sprayed on vertical or hard-to-reach surfaces, used for fast and even coverage in large-scale repairs.
- Pipe Application: Grout is pumped through pipes into voids or foundations, commonly used in soil stabilization or large infrastructure projects.
- Vacuum-Assisted Application: Uses suction to draw grout into cracks or voids, ideal for low-permeability surfaces or delicate structures.
- Tremie Method: Used for underwater grouting, where grout is poured into submerged areas to fill gaps, often used in marine or dam constructions.
Each method is selected based on the application, project size, and site conditions.
Conclusion
Cementitious grouts are versatile, durable, and cost-effective materials essential for various applications. Their ease of use and wide range of applications make them a reliable choice for ensuring long-lasting performance and stability in construction and infrastructure projects.



