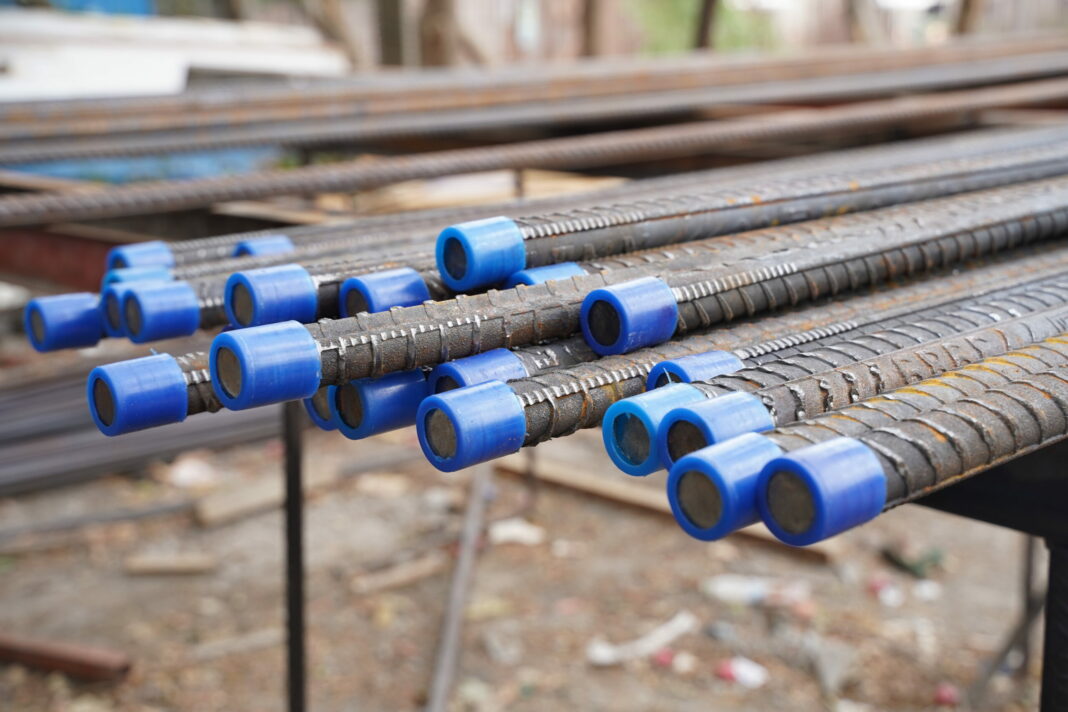
A threaded coupler is used to join reinforcing bars (rebar) in concrete structures, ensuring the continuity and strength of the framework. Made from robust materials like carbon steel or stainless steel, these couplers have internal threads that match the external threads of the rebar, allowing for a secure and seamless connection. This connection enhances the structural integrity and load-bearing capacity of concrete elements, such as columns, beams, and slabs. Threaded couplers are essential in projects requiring extended lengths of rebar, facilitating efficient assembly and reducing the need for overlapping bars, thereby optimizing space and material usage in construction.
Uses of Threaded Couplers in Construction:
- Structural continuity for concrete elements like columns, beams, and slabs.
- Efficient load transfer between connected rebar sections.
- Extension of rebar for tall concrete columns during vertical construction.
- Creation of continuous reinforcement bars in long concrete beams.
- Joining rebar protruding from precast concrete elements such as walls, floors, and bridge segments.
- Addition of new rebar during the retrofitting of existing structures.
- Replacement of damaged rebar sections without extensive dismantling.
- Creation of strong, ductile connections in seismic zones.
- Reliable connections in structures subjected to high loads, such as bridges and high-rise buildings.
- Continuous vertical placement of rebar in concrete core walls for high-rise buildings.
- Joining rebar in large concrete slabs to prevent cracking and distributing loads.
- Extension of rebar cages in deep foundations and piles for robust reinforcement.
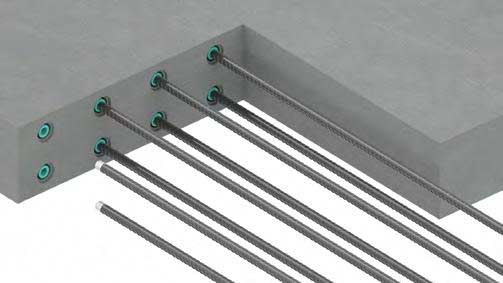
Advantages of Threaded Couplers in Construction
- Provides a continuous load path, improving the overall strength and stability of the structure.
- Minimizes the need for overlapping rebar, saving material and reducing congestion within the concrete.
- Simplifies the connection process, making it quicker and easier compared to traditional lapping methods.
- Accelerates construction timelines by reducing the time required for rebar placement and connection.
- Reduces material wastage by eliminating the need for long overlaps, making the construction process more economical.
- Allows for better use of space within the concrete element, enabling more compact and efficient designs.
- Provides reliable and consistent joint performance, ensuring uniform stress distribution and load transfer.
- Reduces rebar tying and positioning, lowering overall labour costs.
- Suitable for various types of rebar connections, including vertical, horizontal, and inclined joints.
- Enhances quality control by providing factory-manufactured couplers with consistent and predictable performance.
- Offers high tensile and compressive strength, meeting stringent structural requirements.
- Enables flexible design solutions, allowing for modifications and adjustments during construction.
- Provides durable connections that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and long-term stresses.
- By minimizing rebar overlap, it leads to a reduction in the amount of concrete required, further optimizing material usage.
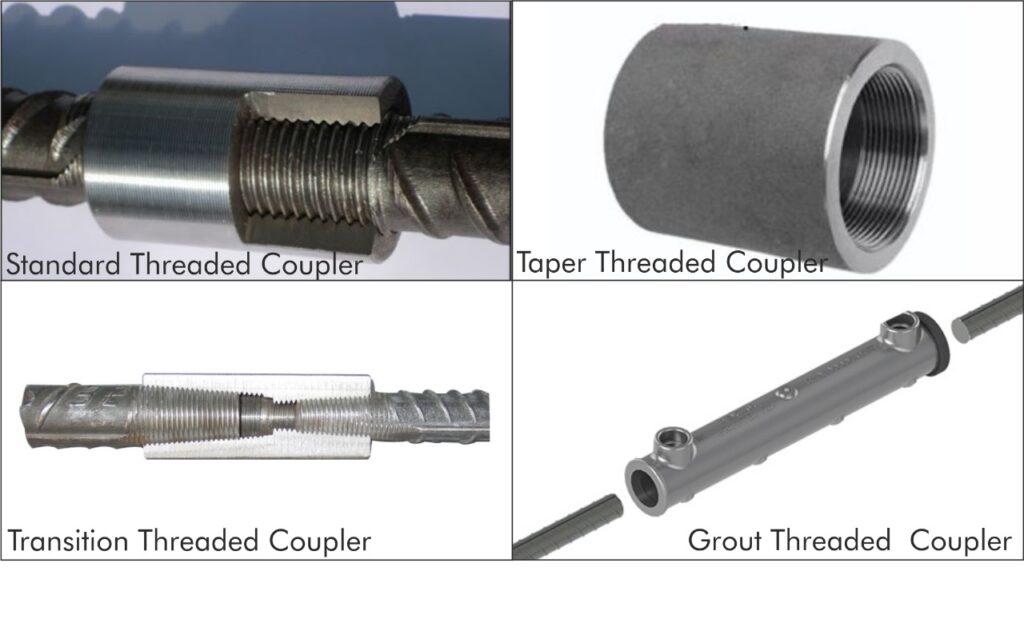
Types of Threaded Rebar Couplers:
1. Standard Threaded Couplers:
Standard threaded couplers are the most common type used in construction projects for general splicing of rebar. They are designed to connect rebar of the same diameter and provide a secure and continuous load path. These couplers ensure that the structural integrity of the reinforcement is maintained, and they are typically used in a wide range of applications, including beams, columns, and slabs. The simplicity and reliability of standard threaded couplers make them a go-to solution for many construction scenarios.
2. Transition Threaded Couplers:
Transition threaded couplers are specifically designed to connect rebar of different diameters. This type of coupler is crucial in situations where rebar sizes need to change due to design requirements or constraints within the structure. By providing a seamless transition between varying rebar sizes, these couplers ensure that the load transfer and structural integrity are maintained. Transition couplers are commonly used in complex structural elements where varying rebar sizes are necessary for optimal performance.
3. Position Threaded Couplers:
Position threaded couplers are used in scenarios where the rebar cannot be rotated, such as in confined spaces or retrofitting projects. These couplers allow for the connection of rebar without the need for bar rotation, making them ideal for applications where precise alignment and minimal movement are required. Position couplers are often used in repair and renovation projects, where existing structures need reinforcement without extensive dismantling.
4. Tapered Threaded Couplers:
Tapered threaded couplers feature tapered threads that facilitate easy alignment and installation. The tapered design ensures a secure and tight connection, which is essential in high-stress applications where precision is critical. These couplers are often used in heavy-duty structural components, such as bridges and high-rise buildings, where the connections must withstand significant loads and stresses.
5. Grout-Filled Threaded Couplers:
Grout-filled threaded couplers combine threaded ends with a grout-filled sleeve for additional bonding. This type of coupler provides enhanced strength and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring extra reinforcement. The grout adds an additional layer of security by filling any gaps and ensuring a robust connection. These couplers are commonly used in precast concrete elements and other high-stress structural applications.
6. Locknut Threaded Couplers:
Locknut threaded couplers incorporate a locknut to prevent loosening under dynamic loads. This design is particularly useful in structures subject to vibrations or cyclic loading, such as bridges, highways, and seismic regions. The locknut ensures that the connection remains tight and secure over time, providing added reliability and safety in critical applications.
7. Swaged Threaded Couplers:
Swaged threaded couplers use a swaging process to deform and grip the rebar ends securely. This method provides a strong connection with minimal rebar preparation, making it a quick and efficient solution for many construction projects. Swaged couplers are ideal for applications where time is of the essence, and the rebar needs to be connected rapidly without compromising on strength.
Application Method of Threaded Rebar Couplers:
1. Preparation and Planning
– Identify the Need: Determine where and why the couplers are required in the rebar layout. This usually involves connecting two pieces of rebar to extend them.
– Choose the Right Coupler: Select the type and size of the treaded coupler based on the diameter of the rebar and the structural requirements.
2. Cutting the Rebar
– Measure and Cut: Measure the length of the rebar needed and cut it to the required length. Ensure that the cuts are clean and perpendicular to the rebar axis.
– Check the Cut Ends: The ends should be smooth, without any burrs or deformation. Use a rebar cutter or a cutting tool designed for this purpose.
3. Threading the Rebar Ends
– Prepare the Ends: Use a rebar threading machine or tool to create threads on the ends of the rebar. The threads should be consistent and fit the coupler.
– Ensure Clean Threads: Check for any debris or damage on the threads. Clean the threads if necessary.
4. Installing the Treaded Coupler
– Position the Coupler: Screw the coupler onto the threaded end of the first rebar piece.
– Align and Screw: Insert the second rebar into the other end of the coupler. Ensure that the threads are aligned properly and screw it in until the coupler is fully tightened.
– Check Alignment: Ensure that the rebar pieces are properly aligned and the coupler is securely fastened.
5. Inspection
– Verify Installation: Inspect the coupler and rebar connection to ensure that it meets the design specifications and is securely fastened.
– Conduct Quality Checks: Perform a quality check to ensure that the connection is robust and free from defects.
6. Finalizing the Installation
– Secure the Rebar: Ensure that the rebar is properly positioned as per the construction drawings and is adequately secured.
– Document the Process: Record the details of the installation process, including the type of couplers used and any issues encountered.
7. Concrete Pouring
– Proceed with Construction: Once the couplers are installed and inspected, you can proceed with the next steps in the construction process, such as pouring concrete.
8. Post-Installation Checks
– Monitor During Curing: Ensure that the couplers and rebar are not disturbed during the concrete curing process.
– Inspect Post-Curing: After the concrete has cured, inspect the couplers and rebar to confirm that the installation has held up as expected.
Conclusion
Threaded couplers have streamlined the way reinforcement bars are joined in construction projects. Their ability to deliver strong, reliable, and efficient connections makes them an indispensable tool in modern construction practices. By offering a precise, high-strength solution compared to traditional methods, threaded couplers not only enhance structural integrity but also streamline the construction process. As the industry continues to advance, the adoption of threaded couplers represents a step forward in achieving both quality and efficiency in construction projects.
Images- viruddhicouplers.com. issuu.com, aleono.com, dextragroup.com, creativeengindia.in





