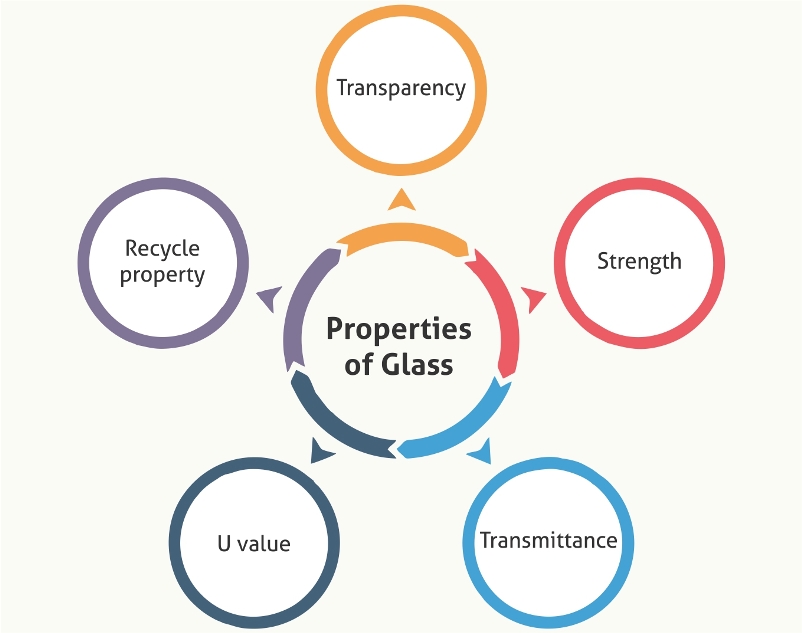
Glass is a hard substance that may be transparent or translucent and brittle. It is manufactured by a fusion process. In this process sand is fused with lime, soda and some other admixtures and then cooled rapidly. Glass is used for architectural purposes in buildings and structures. There are different types of glass used each of them are discussed below:
Sheet or Flat Glass
Flat glass, sheet glass or plate glass is a type of glass that is initially produced in plane form. It is commonly used for windows, glass doors, transparent walls, and windshields. For modern architectural and automotive applications, the flat glass is sometimes bent after the production of the plane sheet. It is commonly used for windows, glass doors, transparent walls, and windscreens. For modern architectural and automotive applications, the flat glass is sometimes bent after the production of the plane sheet.

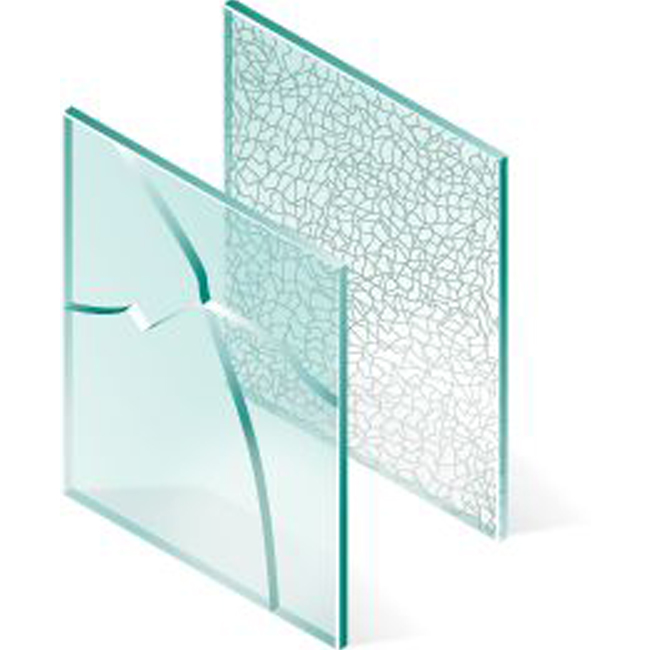
Laminated Glass
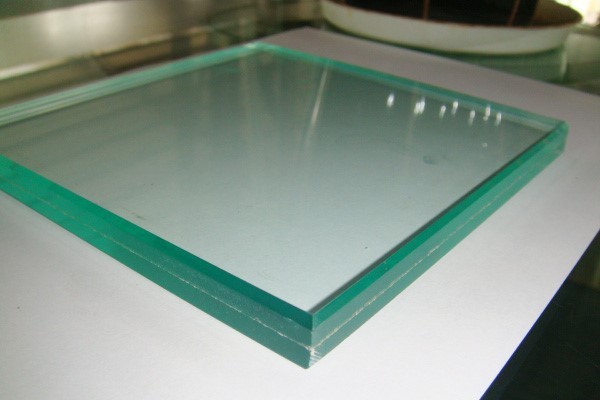
Laminated glass is constructed of two plies of glass that are bonded together with interlayers to form a permanent bond. The interlayers work to support and hold the glass to create a strong, uniformed layer even when broken. Laminated glass comes in varying thicknesses and can be created using different glass combinations or coatings to provide different qualities, such as low emissions or increased insulation. Laminated glass is used when there is a possibility of human impact or where the glass could fall if shattered, and for architectural applications. Skylight glazing and automobile windshields typically use laminated glass. In geographical areas requiring hurricane-resistant construction, laminated glass is often used in exterior storefronts, curtain walls, and windows.
Shatterproof glass
Shatterproof glass is laminated glass; two or more sheets of glass bound together with an invisible interlayer of polyvinyl or resin, though other compounds are sometimes used. The interlayers of shatterproof glass help to reduce sound transmission; your home will be significantly quieter. UV rays are also reduced by this type of glass, keeping the sun from fading fabrics and furniture.

Energy-efficient Glass
Energy-efficient Glass is manufactured by glazing float glass with a special thin coating on one side. Energy-efficient glazing incorporates low-emissivity coated glass to prevent heat from escaping through the windows. This makes the windows highly thermally insulating hence improving the energy efficiency of your building.

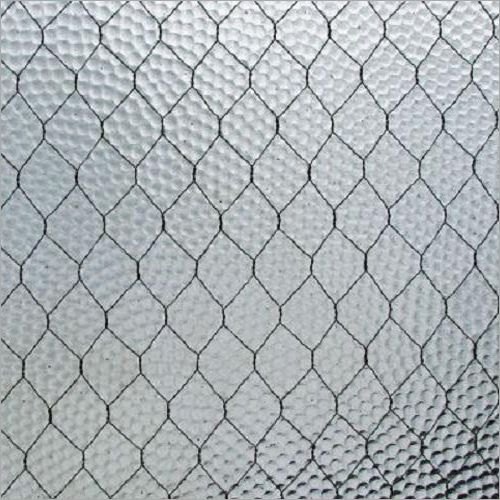
Wired Glass
Wired glass is being used for decades now and it prevents the glass from shattering in case of emergencies. The glass is reinforced with wire mesh during manufacture, which makes it durable, fire-resistant when compared to float glass. It is also known as Georgian wired glass and wire mesh works as a reinforcement. In case due to some higher impact activity the glass breaks, it is held by the wire in position. This lessens the chances of anyone around getting hurt. The wire mesh glass is available in diamond grids and square grids.

Stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material and works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensional structures and sculpture.

Toughened Glass
Toughened glass is physically as well as thermally solid, and research shows that it can withstand surface compression of at least 10,000lbs per square inch, which is why toughened glass is considered to be safety glass. They are also known to be four to five times stronger than annealed glass and three times stronger than heat-strengthened glass. As these glasses are robust, they reduce the risk of damage if they come in contact with a calamity or disaster. Toughened glass is manufactured when regular glass is exposed to extreme heat and then cooled rapidly. Due to this excessive heating and cooling process, the chemical composition of the glass goes through an alteration making it more resilient.

Chromatic Glass
Chromatic glass can control the transparent efficiency of glass and protects the interior from daylight. The chromatic glass may be photochromic which has light-sensitive lamination, thermos-chromatic which has heat-sensitive lamination and electrochromic.

Self-cleaning Glass
Self-cleaning glass is a specific type of glass with a surface that keeps itself free of dirt and grime. The field of self-cleaning coatings on glass is divided into two categories: hydrophobic and hydrophilic. These two types of coating both clean themselves through the action of water, the former by rolling droplets and the latter by sheeting water that carries away dirt. Hydrophilic coatings based on titania (titanium dioxide), however, have an additional property: they can chemically break down absorbed dirt in sunlight.

Float glass
Float glass is a sheet of glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, although lead and other various low-melting-point alloys were used in the past. This method gives the sheet uniform thickness and very flat surfaces. Modern windows are made from float glass. Most float glass is soda-lime glass, although relatively minor quantities of specialty borosilicate and flat panel display glass are also produced using the float glass process. Float glass is essentially a super smooth, distortion-free glass which is used for designing other glass items such as laminated glass, heat-toughened glass, and so on. With a natural greenish hue and translucent nature, it is capable of transmitting the incident light.

Heat-strengthened glass
Heat-strengthened glass is similar to tempered glass except that the cooling is done at a much slower pace. Annealed glass is heated to approximately 650-7000C, but the cooling process is slower than that for tempered glass. Heat-strengthened glass is about twice as strong as annealed glass of the same size and thickness. Heat-strengthened glass is a semi-tempered glass that retains the normal properties of ordinary float glass.

Conclusion
Given above are different types of glass that could be used for building architecture. Glass is used as a transparent glazing element in the building envelope. This includes windows in external walls and internal partitions.





