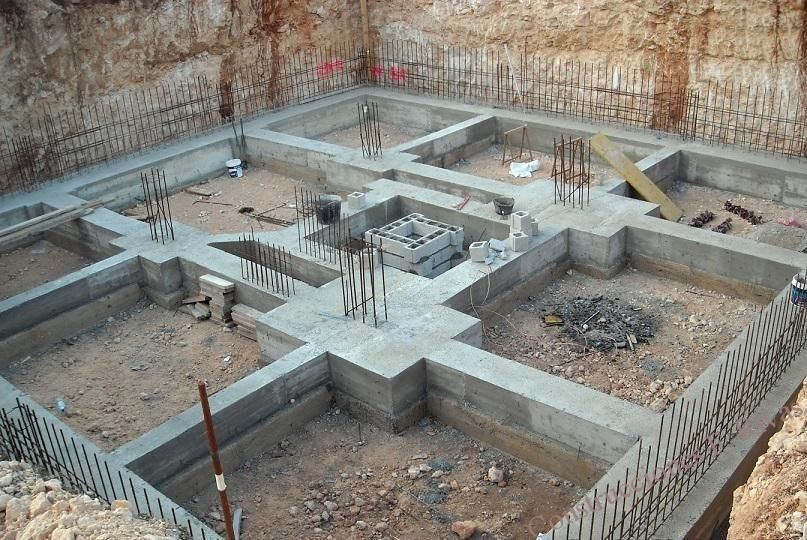
Foundation is the main supporting component of any building structure. It is the lowest part of the building which is in contact with soil and transfers all structural load to soil safely. The purpose of a foundation is to hold up and hold together the structure above it. Contrary to our everyday experience the ground is not quite still and in many cases not totally solid. A house which is just plonked down on bare earth is more likely to be cracked or damaged over time by natural forces. A properly-built foundation increases the amount of abuse a house structure can take and remain safe for the people inside it.
Types of Foundation In Building and Structures
Foundations are classified as shallow and deep foundations. Types of foundations under shallow and deep foundations for building construction.
Shallow foundations
Shallow foundations are those found near to the finished ground surface; generally where the founding depth (Df) is less than the width of the footing and less than 3m. These are not strict rules, but merely guidelines: basically, if surface loading or other surface conditions will affect the bearing capacity of a foundation it is ‘shallow’. Shallow foundations (sometimes called ‘spread footings’) include pads (‘isolated footings’), strip footings and rafts. Shallow foundations, often called footings, are situated beneath the lowest part of the structure. A footing is the first constructed element of a structure which is built after excavating the ground. In general, the depth of a shallow foundation is less than its width.
Shallow foundations are commonly used as they are the most economical foundation system and are relatively easy to construct. A careful investigation of the foundation site and detailed information of the subsurface stratum is necessary to design the foundation and avoid any future degradation of the foundation performance.
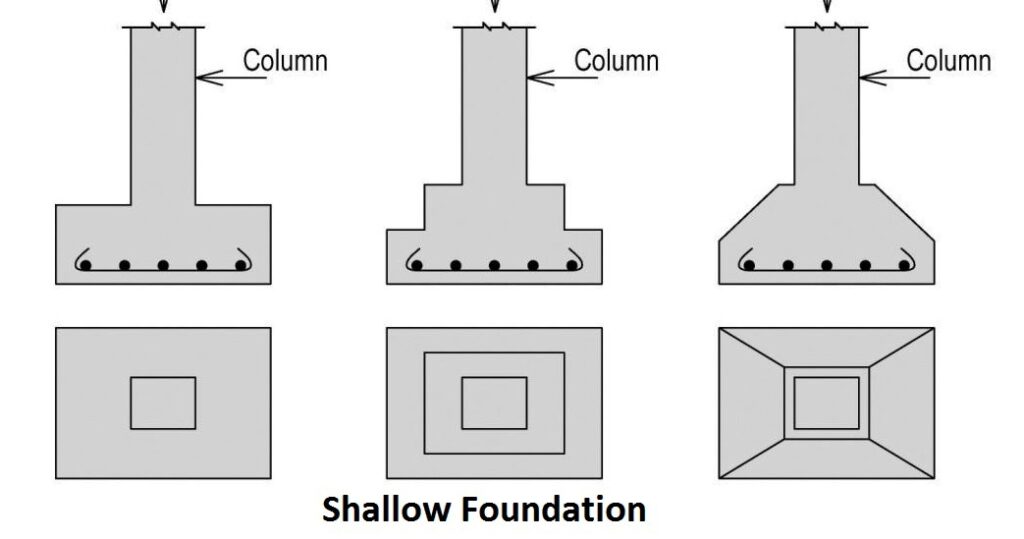
Different types of shallow foundations;
- Isolated footing
- Combined footing
- Strip foundation
- Raft or mat foundation
Isolated footing
The isolated footing is used to support individual columns. They can be either of steeped type or have projections in the concrete-base. it is provided in cases where the bearing capacity of the soil is good at shallower depths. It is easy to construct.Generally foundation is designed to satisfy the basic three criteria, the foundation must be aligned correctly in both the vertical and horizontal direction, should be safe from bearing capacity failure and and safe from extreme settlement. Loads on the foundation are self-weight loads, live loads, earthquake loads, earth pressure, and water pressure.
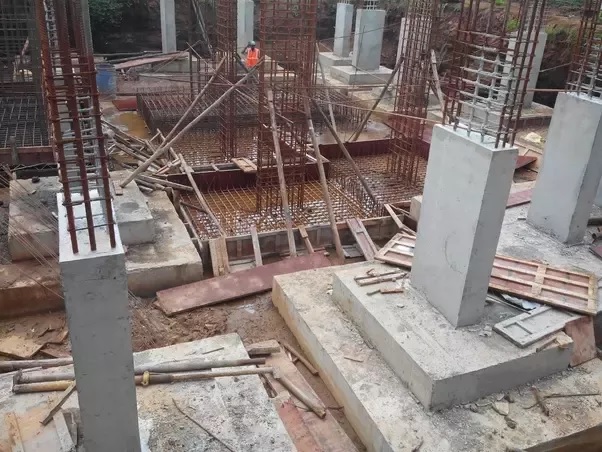

Combined footing
Combined footing supports the land of two or more adjacent columns. There are two types of combined footing, rectangular combined footing and trapezoidal combined footing. Combined footings are provided when distance between two columns is small and soil bearing capacity of soil is lower and their footings overlap with each other.When two columns are close together and separate isolated footings would overlap, in such case, it is better to provide a combined footing than isolated footing.

Strip foundation
Strip foundations are used where the soil is of good bearing capacity. The key sizes of a strip foundation for concrete cavity wall construction and timber frame cavity wall construction are similar. The size and position of the strip is directly related to the overall width of the wall. Strip foundations can be used for most subsoils, but are most suitable for soil which is of relatively good bearing capacity. They are particularly suited to light structural loadings such as those found in many low-rise or medium-rise domestic buildings – where mass concrete strip foundations can be used. In other situations, reinforced concrete may be required.
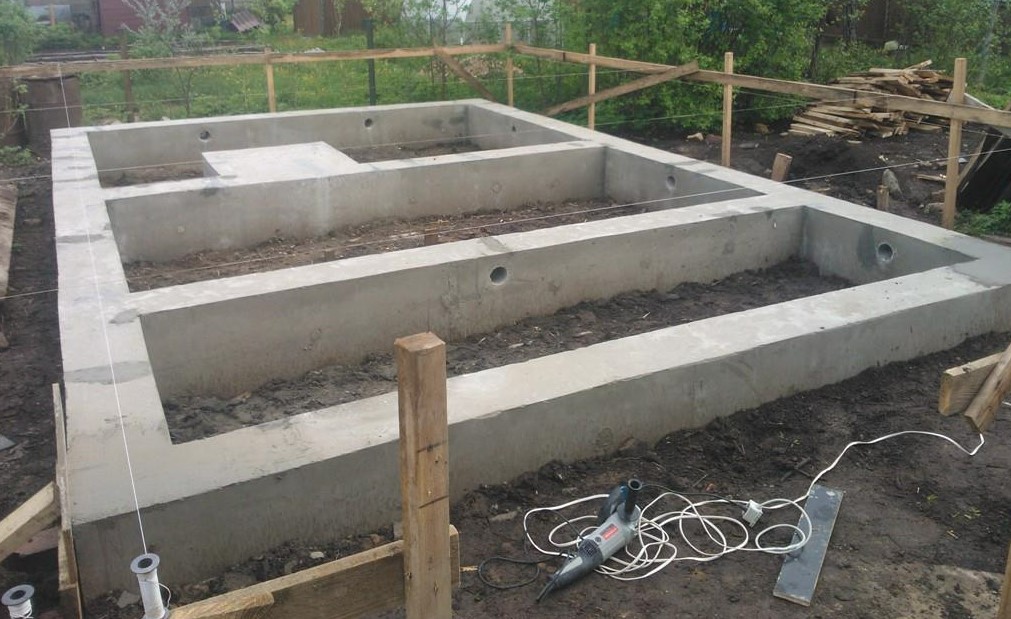

Raft or Mat foundation
Raft foundation is the continuous slab, which is resting on the hard soil, which extends over the entire building footprint. It declines the contact pressure in comparison with conventional strip or trench footing. Raft foundation is also known as Mat foundation. Raft foundations are used to spread the load from a structure over a large area, normally the entire area of the structure. They are used when column loads or other structural loads are close together and individual pad foundations would interact. A raft foundation normally consists of a concrete slab that extends over the entire loaded area. It may be stiffened by ribs or beams incorporated into the foundation. It has the advantage of reducing differential settlements as the concrete slab resists differential movements between loading positions.

Deep foundations
A deep foundation is a type of foundation which is placed at a greater depth below the ground surface and transfers structure loads to the earth at depth. The depth to width ratio of such a foundation is usually greater than 4 to 5.
The construction process of a deep foundation is more complex and more expensive than shallow foundations. However, when dealing with poor soil conditions at shallow depth, large design loads, and site constraints, a deep foundation is likely to be the optimum solution. Deep Foundation is used Where the bearing capacity of the soil is very low. The load coming from the superstructure is further transmitted vertically to the soil
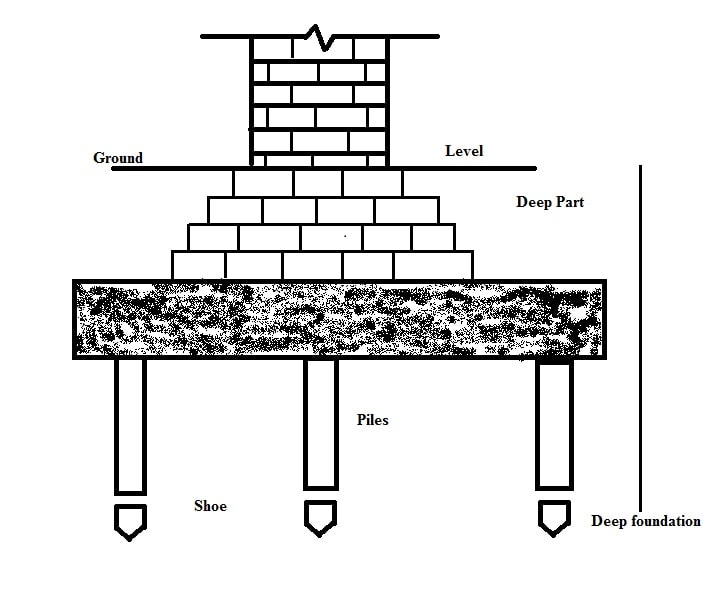
Different types of deep foundations
- Pile foundation
- Drilled Shafts or caissons
Pile foundation
Pile foundations are principally used to transfer the loads from superstructures, through weak, compressible strata or water onto stronger, more compact, less compressible and stiffer soil or rock at depth, increasing the effective size of a foundation and resisting horizontal loads. They are typically used for large structures, and in situations where soil is not suitable to prevent excessive settlement. As pile foundations carry a lot of load, they must be designed very carefully. A good engineer will study the soil the piles are placed in to ensure that the soil is not overloaded beyond its bearing capacity.
There are two fundamental types of pile foundations, End Bearing Piles and Friction Piles. In end bearing piles, the bottom end of the pile rests on a layer of especially strong soil or rock. The load of the building is transferred through the pile onto the strong layer. In a sense, this pile acts like a column. Friction piles work on a different principle. The pile transfers the load of the building to the soil across the full height of the pile, by friction. In other words, the entire surface of the pile, which is cylindrical in shape, works to transfer the forces to the soil.
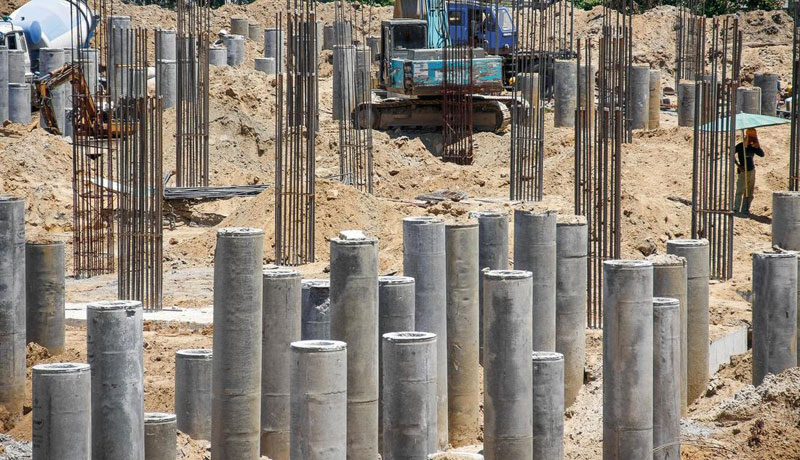

Drilled Shafts or caissons
Drilled shaft casings are also referred to as caissons, bored piles, or drilled piers. They are rigid, high-capacity, cast-in-place, concrete, deep-foundation solutions. They are used to support structures with large axial and lateral loads by drilling cylindrical shafts into the ground which are then filled with concrete. These elements and processes provide foundation and earth retention support for a broad range of structures and construction projects. Drilled-hole shafts like this are deep-foundation solutions capable of bearing large loads with high lateral resistance and are often designed for bridges and other large structures.
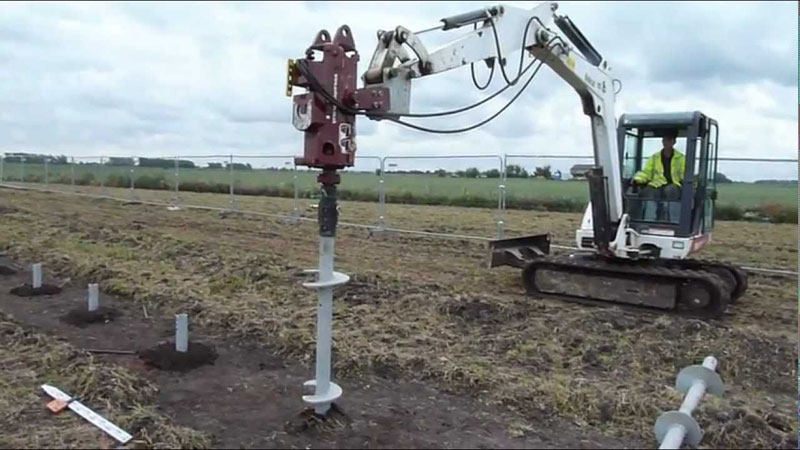

The purpose of a drilled shaft is to transmit a structural load to the shaft’s base, which may be bedrock or another hard stratum. In essence, a drilled shaft is primarily a compression member with an axial load applied at its top, a reaction at its bottom, and lateral support along its sides. Drilled shafts are constructed by using auger drill equipment to form a hole in the soil. Soil is removed from the hole during drilling, in contrast to the driven pile, which only compresses soil to the side. Drilled shafts are a popular type of deep foundation for several reasons. Drilling equipment is relatively light and easy to use compared to pile-driving equipment, resulting perhaps in lower construction costs.





