India is a heritage of old buildings and Structures. These buildings have aged more than 30 years. These buildings have reduced Strength due to Material Deterioration. If further use of such damage structure is continued it may cause severe loss of life and property. A structural Audit is the overall Health Check-up of a building to ensure that the building is safe and has no risk. It also suggests some Repair to increase the Serviceability of the building. A structural audit, therefore, is important.
A structural Audit is an important tool for knowing the real status of the heritage structures. It ensures that the building and its premises are safe and have no risk. It analyses and suggests appropriate repairs and retrofitting measures required for the buildings to perform better in its service life. A structural audit is done by an experienced and licensed structural consultant.

Purpose of Structural Audit of heritage structures
- To understand the condition of building.
- To find critical areas to repair immediately.
- To comply with Municipal or any statutory requirements.
- To enhance the life cycle of a building by suggesting preventive and corrective measures like repairs.
- To know the health of your building and to project the expected future life.
Methodologies for the structural audit of heritage structures
Destructive testing
To verify the integrity of a component, it is always possible to cut or section through the components and examine the exposed surfaces. Components can be pulled or stressed and pressurized until failure to determine their properties of strength and toughness. Materials can be chemically treated to determine their composition. These are some forms of destructive testing. Unfortunately, this approach of destructive testing renders the component useless for its intended use as against non-destructive testing which can be performed on the components and machines without affecting their service performance.
Different types of destructive testing
Stress Testing
It is a form of testing that is used to determine the stability of a given system or entity. It involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, to observe the results. Stress testing may have a more specific meaning in certain industries, such as fatigue testing for materials.

Crash Testing
It is a form of destructive testing usually performed to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for automobiles or related components. Some of the examples are Frontal-Impact Tests, Offset Tests.
Side-Impact Tessting
Rollover Tests, Roadside hardware crash tests, etc. The tests are not discussed here as it is beyond the scope of this presentation.
Hardness Testing
Hardness refers to various properties of matter in the solid phase that gives it high resistance to various kinds of shape change when force is applied. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds. However, the behavior of solid materials under force is complex, resulting in several different scientific definitions of what might be called “hardness” in everyday usag

Non Destructive testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is a wide group of analysis techniques used in the science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component, or system without causing damage. The terms Non-destructive examination, Non-destructive inspection and Non-destructive evaluation are also commonly used to describe this technology because NDT does not permanently alter the component being inspected, it is a highly valuable technique that can save both money and time in product evaluation, troubleshooting, and research. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic, magnetic particle, liquid penetrant, radiography, remote visual inspection (RVI), eddy current testing.
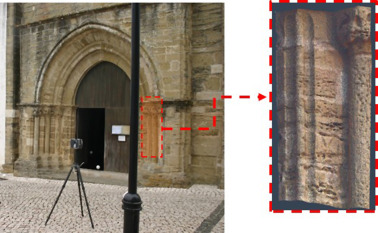
Different types of non- destructive testing
Rebound Hammer testing
It is used to check surface strength/Soundness of cover concrete Which in turn can be converted to the indicative compressive strength of concrete. It is also called the Schmidt hammer test that consists of spring controlled metallic equipment that slides on a plunger within the tubular housing. The plunger is pressed against the concrete surface so the spring-controlled mass bounces back. The extent of rebound is a measure of surface hardness which is indicated on the graduated scale. The result thus achieved is called rebound number/rebound index. Concrete having lower strength will have lower stiffness & thus will absorb more energy to result in yielding a lower rebound number.

Ultrasonic pulse velocity testing
It is an in-situ test to check the quality of concrete & natural rock/stones by passing an ultrasonic sound wave & checking its velocity. It indicates homogeneity of concrete/stone, evaluates dynamic modulus of elasticity, estimates the depth of cracks, honeycombs & can be used to check the effectiveness of repairs.

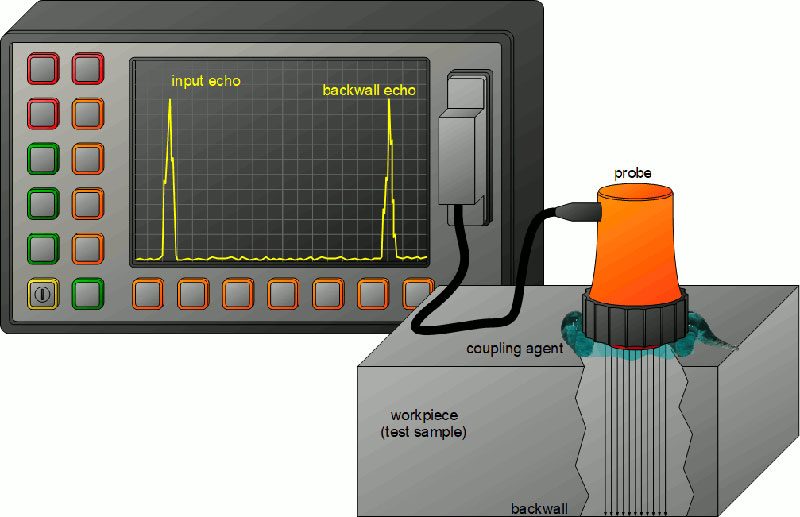
Ultrasonic echo testing
For this test, frequency is used for concrete 500 Hz as max. & 20 Hz as a minimum. UPV needs access on both sides of the concrete member to get reliable information while this system is one dimensional. Stress waves reflected from inherent defects such as crack or void are determined.
Half- Cell potential testing
This method detects negative charge in reinforcement causing the likelihood of corrosion possibility which is measured using half cells. At Anode~Ferrus becomes ferric while at cathode, Water + oxygen converts into 4OH.

Digital concrete microscope testing
This method is useful in understanding concrete density, particle size distribution, inherent cracks/honeycombs & fine to coarse aggregate ratio while inspecting concrete after core cutting. Newer versions are available where cameras can be inserted in concrete by drilling holes.
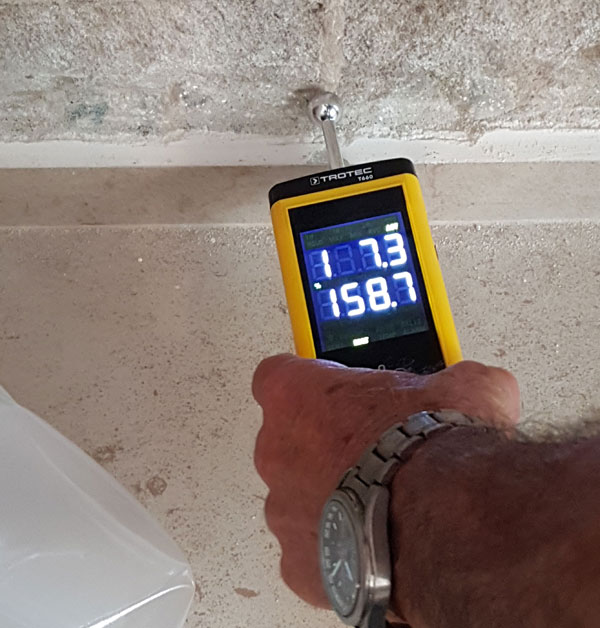
Moisture meter testing
This test is available in a digital version with a metal probe showing results in % for concrete & wood. Useful to detect leakage locations having the highest % moisture. This avoids unnecessary speculations & breaking.

Digital thermal imaging testing
This is an advanced test rather than a moisture meter test which demonstrates leakages in a more accurate manner depending on the thermal conductivity of different building materials used in construction.

Profometer testing
It is to check diameter & spacing of embedded reinforcement & depth of cover concrete. It has a memory storage & printing facility to avoid remembering results or manipulation.

Sonic Echo testing
It is used to calculate the time of impact generation & vertical movement of pile/raft concrete due to impact are recorded by digital data acquisition devices like oscilloscopes periodically. Results will tell the story of the discontinuity/integrity of the foundation.

Stress wave testing
This is used to determine the stiffness profile of soil, asphalt or concrete pavements besides concrete str. Members & also for checking changes in elastic properties of concrete during curing, detection of voids & internal damages.
Probe penetration testing
This test has much higher energy than rebound hammer, but results are equally affected by the presence of aggregates, surface undulations, crack, honeycomb & bleeding/segregation, age of concrete etc. This is a partially destructive test causing holes in concrete which must be filled with polymer mortar/epoxy.

Ground Penetrating Radar testing
This test is useful in detecting subsurface objects embedded in rock, soil, ice, freshwater, pavement & structures using electromagnetic energy using high-frequency radio waves from 10 Mhz to 1 GHz i.e. 1000 Mhz. It is also useful in detecting changes in materials properties, voids, cracks etc.

Linear polarisation testing
This test is used for corrosion monitoring generally used for marine structures reinforcement. A small change in half cell potential of the corroding bar is measured in the polarization resistance test. This enables periodic enhancement in corrosion rate/speed at which bar corrodes so life can be predicted as per dia. / quantity of metal loss.
Digital Elcometer testing
This test is useful in checking film thickness of all types of paints like Acrylic, Alkyd, Epoxy, PU etc. on metallic surfaces. It can check uniformity of film thickness that talks about precision in application.

Digital metal hardness testing
This test is useful for ferrous & nonferrous metal surfaces to measure dry film thickness of paint/coating.

Conclusion
Buildings observed having cracks or leakages which are indicative of its health hazard, thus calling for inspection through an expert agency. This may happen even to buildings that are newly constructed, a few months or years back. This methodology keeps you aware of the state of the heritage buildings.
Image Source: sciencedirect.com, iamcivilengineer.com, tuv.com, avonprojects.in, masonrysolutions.com, tec-science.com, geomarineindia.com, buildingconservation.com, wikipedia.com, proceq.com, ftandc.com, gharpedia.com, fprimec.com, elcometer.com, mistrasgroup.com, geocorpinc.com, mumbailive.com





