
Low free (LF) technology can be used to produce new MDI polyurethane (PU) prepolymers for use in the construction industry with a free isocyanate content of less than 0.10 percent. Therefore, these LF MDI prepolymers meet strict standards with regard to occupational safety and industrial hygiene and can be classified in low hazard classes. The initial application focus is on adhesives and sealants as well as 1K foams.
The construction industry is currently experiencing a radical change. Buildings should be energy-efficient and made of durable, renewable and health-neutral materials. Future trends include the Smart Home, modular construction and 3D printing of building components. The Urethane Systems business of LANXESS is addressing these developments. The company has been a partner to the construction industry for decades, for example with products for plastic roofing membranes, for crack sealing in masonry, for coating a wide variety of floors and for the thermal insulation of window and door profiles.
Global presence and development expertise
With the acquisition of Chemtura, LANXESS has set up the Urethane Systems business as an independent, entrepreneurial business unit. It regards itself as a systems supplier for the global PU industry. It offers complete systems for casting, coating, adhesive and sealant applications. Urethane Systems is one of the world’s leading suppliers of conventional and low-free prepolymers as well as aqueous specialty polyurethane dispersions (PUD) – with a particular focus on solvent-free and LF monomer systems. It has production facilities worldwide – in Brazil, the United States, China, Italy and England, for example (Fig. 1). Its global research, development and innovation center is located in Naugatuck, Connecticut. For example, new prepolymers blocked with ε-caprolactam have recently been developed there. They can be used to formulate one-component and therefore easy-to-process reaction systems.
Prepolymers are key to superior performance
Another innovation is the new generation of prepolymers developed for the construction industry with a very low content of free isocyanate monomers. They are marketed under the trade name Adiprene LF and are primarily intended for use in reactive hot-melt adhesives, ambient-drying adhesives, sealants and one-component foams (1K).
Adhesives and sealants based on LF prepolymers offer optimum industrial hygiene. LF technology reduces the concentration of free isocyanate in the prepolymer to below 0.10 percent for a broad range of isocyanates, including MDI. This results in prepolymer building blocks and end products that meet the requirements of lower hazard classifications and the latest regulatory trends. The processor can significantly reduce the technical and administrative expense for health, safety and environmental protection and improve industrial hygiene by eliminating raw materials containing elevated levels of hazardous isocyanates during the production process.
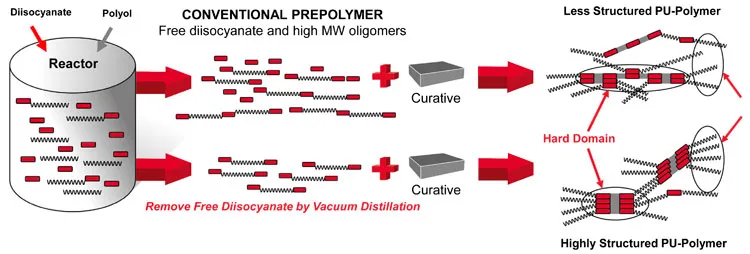
Highly ordered domain structure
The use of LF isocyanate prepolymers results in a superior performance of the PU formulated products. The LF prepolymers drive controlled morphology and allow for tailored properties and processing consistency. Furthermore, they achieve a narrow molecular weight distribution, enhanced physical cross-linking and highly structured phase segregation between hard and soft segments (Fig. 2). The enhanced phase segregation improves the physical and mechanical properties of the material. For example, PU systems formulated with LF prepolymer technology can exhibit an excellent flexibility and tear strength while still maintaining a high tensile strength. This pays off in applications with high mechanical loads and long lifetime.
Constant isocyanate content, broadly adjustable viscosity
By use of LF technology the viscosity of the prepolymers can be controlled. This is a major strength of Adiprene LF. Prepolymer viscosity can be tailored to meet existing processing conditions and equipment while meeting or exceeding application demands. By controlling the morphology, it is possible to vary the viscosity over a wide range at a constant isocyanate content (NCO content). This allows important product properties – such as wetting behavior or coverage rate – to be optimized for the application. Higher viscosities may be required for prepolymers, for example, which are converted into foams with propellants. In the case of hot melt adhesives, for example, low viscosities generally facilitate the processing of prepolymers and final systems.
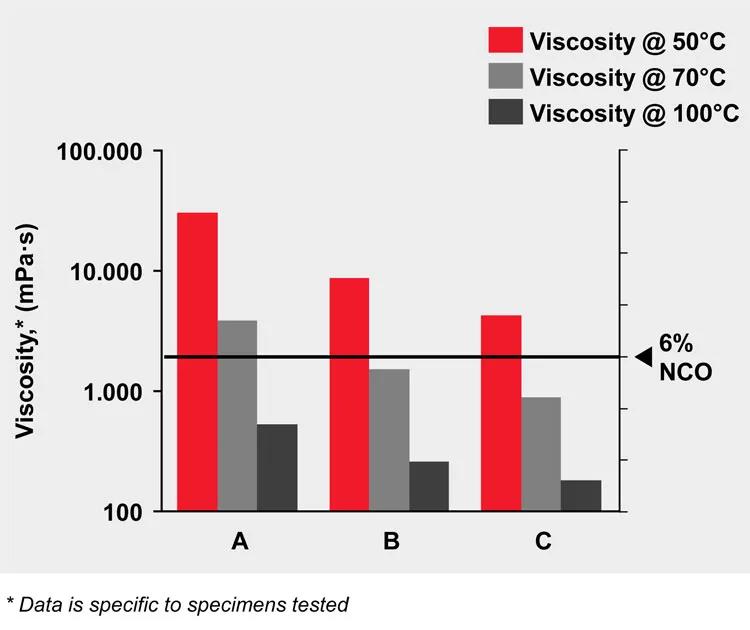
How viscosities can be varied is shown by the example of a polypropylene glycol-based LF prepolymer based on MDI (methylenediphenyl diisocyanate) (Fig. 3). These systems are well suited, for example, for the production of 1-component foams. Urethane Systems was able to formulate three prepolymer systems with viscosities of about 50,000 MPa*s, 9,000 MPa*s and approx. 6,000 MPa*s (50°C) at a fixed NCO content of six percent. The relative difference in viscosities stays constant over a wide temperature range up to 100°C (Fig. 3).
LF prepolymers with highly crystalline polyols for hot melt adhesives
The low viscosity of LF prepolymers also has a benefit in reaction systems for reactive hot melt adhesives. They are often formulated with prepolymers consisting of fast-crystallizing polyester polyols with high molecular weights. The early crystallization during the cooling of the PU polymer ensures a high initial bond strength of the adhesive systems. Even when solid crystalline polyester polyols are used, LF technology can still be employed to make prepolymers for adhesive systems that are easy to process at low temperatures. These also exhibit good wetting and flow properties and require only low joining forces.
Urethane Systems, for example, has developed MDI-based LF prepolymers that have a free NCO content of less than 0.10 percent combined with low viscosity, thereby allowing the resulting reactive hot-melt adhesive systems to be formulated without the need for diluting additives.
“Well-filled construction kit”
In addition to curatives and additives, Urethane Systems offers a wide range of isocyanates and polyols that can be used to customize LF prepolymers with low NCO contents according to the modular design principle – whether for industrially processed one-component foams or for ambient or moisture-cured, field applied sealants. In addition to LF MDI and LF TDI prepolymers, Urethane Systems also markets aliphatic LF HDI (hexamethylene diisocyanate) and LF IPDI (isophorone diisocyanate) prepolymers, from which light-stable and weather-resistant adhesives and sealants can be produced. A further focus is on a range of specialty LF pPDI (p-phenylene diisocyanate) prepolymers for products exposed to extreme heat and chemicals. LANXESS relies on more than 60 years of experience in structure-property relationships in PU material formulation, process engineering and manufacturing technology when it comes to the development of customized polymer systems. The backbone of customer service are the application development centers operated in all major economic regions worldwide.
Outlook
A central focus of LANXESS Urethane Systems’ development work is to expand the product range of new sustainable LF prepolymers with low free isocyanate content (below 0.10 percent). This aims to improve safety, industrial hygiene, and performance in the processing and application of PU systems. Another focus is on adding further valuable properties to PU prepolymers to enhance their performance and range of applications. One such approach is the incorporation of 2,4-MDI into the prepolymer backbone to tailor reactivity and viscosity in adhesive and sealant applications.
Authors:Ronald M. Emanuel, Jr., Senior Scientist at the global research, development and innovation center in Naugatuck, Gerry King, Head of Application Development in Europe, and Dr. Polina R. Ware, Head of Global R&D, all Urethane Systems Business Unit, LANXESS AG.

